Humus ensures good plant growth. How you can ensure a rich yield of humus in your garden, you will find out in our article.

The raw material for humus is dead organic matter. However, this can either be converted into humus or broken down into nutrients. The formation of humus is called humification, and the breakdown and release of nutrients is called mineralization. The two processes should be in a balanced relationship to each other, so that there is sufficient humus and sufficient nutrients are released to be available to the plants growing in the soil can.
If you want to learn more about the processes of mineralization and humification, then you can more information here Find.
contents
-
Humus management: instructions
- 1. Soil pH
- 2. Floor ventilation
- 3. Nutrient content of the soil and the substrate
- 4. Soil temperature
- 5. water
- Humus management: our conclusion
- Buy and receive humus
The humus economy is now concerned with balancing the relationship between humus formation and nutrient release. This ratio is influenced by many factors, which we will explain to you in more detail below. Soil organisms are always involved, whether humification or mineralization depends largely on their activity.
Humus management: instructions
By observing the factors listed and described in detail below, you can actively influence and increase the humus formation of your soil.
1. Soil pH
Most soil dwellers love a neutral pH value, so the application of lime, which raises the pH value slightly, can increase the activity of soil organisms. This can then lead to increased mineralization and possibly even to humus degradation. Conversely, a low pH value lowers the activity of microorganisms, sometimes even so much that the organic material is only decomposed by a few fungi. Very acidic soils are therefore often rich in humus, but poor in nutrients, because the organic material cannot be mineralized. This fact can be observed, for example, in the tropics or on acidic forest soils, where thick layers of only slightly decomposed organic material and so-called raw humus can be found.
If you want to influence the pH value, it makes sense to determine beforehand what pH value your own soil has. To do this, you can either send soil samples to a laboratory (for example at the Raiffeisen Laboratory Service) or test the soil yourself (for example with pH indicator sticks or a pH measuring device) or you can find pointer plants in your own garden that show approximately how acidic the soil is is.
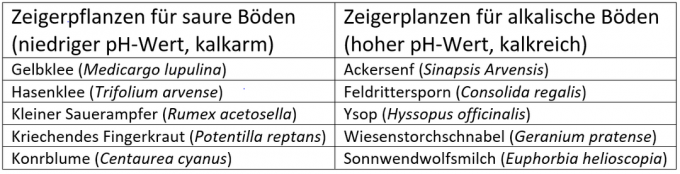

Since the pH value of the entire soil can hardly be influenced, the information should be dealt with as follows:
Soils that are already alkaline should on no account be whitewashed. The microorganisms are already promoted by the high pH value. If calcium is applied as a plant nutrient, then it should be applied in a slowly degradable form such as cottage lime. If the soil is acidic (pH below 7), liming can be done without hesitation in order to fertilize calcium as a plant nutrient or to stimulate mineralization.
Nevertheless, in this case, too, you should refrain from using it immediately after organic fertilization (for example with Compost or horse droppings), as otherwise the soil life mineralises so quickly that a lot of humus is lost goes. It is better to wait at least a year before liming after having fertilized in large quantities organically.
Some fertilizers also affect the pH of the soil: nitrogen in the form of ammonium makes the soil more acidic, while nitrogen in the form of nitrate makes it more alkaline. So when using these types of nitrogen fertilizers one should think about alternating the form of nitrogen application if the pH of the soil is not to change.
2. Floor ventilation
Most organisms that deal with the organic matter in the soil are aerobic (from the Greek “aer” = air), which means that they need oxygen to survive. The more oxygen there is in the soil, the more active they are. A compacted or wet soil contains very little oxygen, so that a large number of microorganisms die and less organic material is converted. To understand this, one only has to imagine a bog: This is the only reason why the peat can be so thick Layers arise because the breakdown by microorganisms is inhibited by the lack of oxygen is.

There are many studies that show that the humus content of soils decreases when they are cultivated. This is due, among other things, to the intensive processing. The constant turning, cultivating, plowing and digging means that much more oxygen gets into the soil, so that the aerobic soil life is at its best and a lot of humus is converted. Although this also releases many nutrients, the humus content drops. Some farmers are now using a more gentle method instead of “turning soil cultivation”, in which the soil is turned over Processing in which less turning with a plow or tiller and more superficially loosened, the so-called "conservation" Tillage ".
If you want to keep your humus, you don't have to do too frequent milling or other work where the The soil is too well ventilated and it is better to dig the bed only once a year with a digging fork in order to close the soil loosen. The superficial loosening before sowing, when working in fertilizer or hoeing against weeds and water loss is of course allowed at any time.

3. Nutrient content of the soil and the substrate
The living space and at the same time the food of the organisms is called “substrate”. The organic material that is decomposed consists not only of nutrients, the largest proportion is carbon. The ratio between carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) is called the C / N ratio. Nitrogen is the nutritional basis of many soil organisms, while carbon is the "framework" from which everything organic is built, for example sugar, starch or cellulose in plant cells.
If the C / N ratio of the substrate is very high (i.e. a lot of carbon, little nitrogen), they have Soil organisms have a lot of implementation work to do - but little nitrogen as an energy source to cope with this job. As a result, this material is not mineralized as quickly, so that in this case humus is more likely to develop.
But if the C / N ratio of the substrate is small (i.e. a lot of nitrogen, little carbon), they have Soil organisms have enough food in the form of nitrogen to immediately mineralize a lot of material - so it is created less humus. Instead, lots of nutrients are released. The carbon structure of the converted material is called carbon dioxide (CO2) dismiss and leave the floor. In general, it can be said that woody plant material tends to have a high C / N ratio, while green, soft plant material has a low C / N ratio.
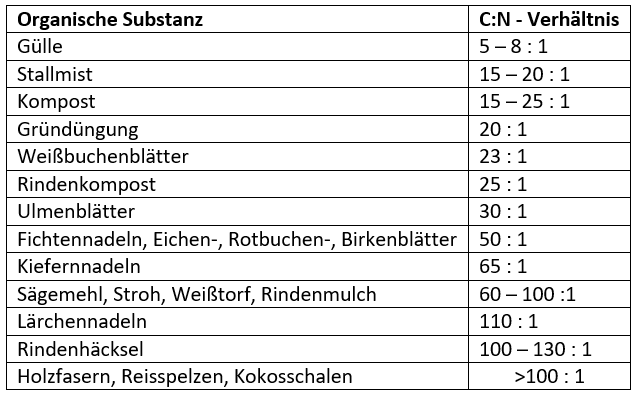
Tip: From a C / N ratio of over 25: 1, the degradation is inhibited, so that humus is more likely to develop. At C / N ratios below 20: 1, the organically bound nitrogen is quickly released.
So when you fertilize your soil, you should pay attention to the C / N ratio: if you add a lot of nitrogen, you increase the activity of the soil organisms. To prevent them from degrading your humus as a result, it is very important to offer them new carbon in the form of hard-to-degrade organic material. For example, it would be possible to work in finely chopped garden waste, wood chips, bark mulch or straw at the same time. You can also subject this garden waste to rotting: Through the rotting process (for example on a compost heap) this becomes C / N ratio shifted a little bit in the direction of N, can be worked better into your soil due to the softer structure and it becomes faster Implemented humus.
Organic material with a very small C / N ratio is quickly mineralized due to the high nitrogen content, it should be treated more like a kind of fertilizer. Materials with a low C / N ratio are, for example, vegetable waste from the kitchen, liquid manure or manure and freshly cut lawns.
If possible, you should fertilize organically - compost, horse manure with straw and also organic commercial fertilizers have a C / N ratio that promotes humus formation.
4. Soil temperature
Soil organisms like it quite warm. Soil activity increases with temperature, provided the soil is sufficiently moist. It is actually very positive when a floor warms up slightly. Plants then grow earlier in the year and faster on it, and the soil organisms provide them with nutrients. It is problematic, however, when a soil without vegetation warms up and the soil organisms are busy supplying nutrients that no plants can absorb.
In this case it can happen that nutrients are washed down with the rain or irrigation water where the plants can no longer use them and, in the worst case, the groundwater affect. At the same time, the humus in the soil escapes into the air in the form of carbon dioxide. If no parts of the plant reach the ground that can replace the carbon that has disappeared, then the humus content of the soil naturally falls. For this reason, you should avoid leaving the soil completely bare, in case of doubt you can sow green manure. On the one hand, the plants absorb nutrients, on the other hand, they fix the carbon from the air so that it gets back into the soil when the green manure is incorporated later. Their leaves also shade the ground so that it stays cooler. If you cannot or do not want to apply green manure, you should think about covering the area with a layer of mulch.

5. water
Like all living things, the soil dwellers also need water, not only because it is part of their bodies, but also because they can move around better in the moist soil. In addition, many important chemical processes can only take place if it is humid enough. In soils that are too dry, little or no organic material is converted. Too much water, on the other hand, causes the soil dwellers to run out of oxygen, which also leads to an inhibited conversion. How much water is applied to a soil depends, of course, above all on the plants that grow on it. To orientate oneself to the soil organisms for this factor would not be optimal. So you can always pour as needed.
Humus management: our conclusion
If you want to build up humus, you should lime sparingly so as not to increase the pH value of your soil too much. In order to avoid excessive ventilation, turning and mixing as little as possible should only be worked on loosely. It is very important to ensure that there is an even supply of hard-to-break organic material with every fertilization. In addition, the ground should never lie fallow and be unshaded as far as possible.
tip: If you want to stimulate soil life, you can also use a so-called soil activator. Our Plantura Organic soil activator contains living mycorrhizal fungi, which stimulate the activity in the soil and thus ensure a healthy and fertile subsoil in the long term.
Buy and receive humus
Promoting humus formation in your garden as described above is too time-consuming, tedious and complicated for you? Then of course you can simply buy humus. We have what needs to be considered in a separate article summarized for you.



