Soil pH is a crucial factor in plant growth—as many gardeners know. We'll explain to you simply what soil pH has to do with acidic soil and alkaline soil and how you influence acidity.

Soil pH is a single number that tells you whether a soil is acidic, neutral, or alkaline. The letters pH stand for potentia Hydrogenii, which translated from Latin means "potential/power of hydrogen" and describes the content and activity of hydrogen in the soil. The more hydrogen there is in the soil, the more acidic it is and the lower the measured soil pH value.
But of what interest is the pH value of the soil or even the content of hydrogen ions for a gardener?
pH influences a number of chemical and biological processes in the soil. Nutrient availability, activity of soil life, crumb structure and thus directly plant growth depend on the acidity of the soil. It is not for nothing that an optimal soil pH value can be found for all crops, in which they can grow as best as possible.
"Contents"
-
Determine the pH of the soil
- pH soil test
- Indicator plants for soil pH
-
What does my soil pH mean?
-
Acid soil (pH < 5.5)
- Why is the soil becoming acidic?
- What plants grow in acidic soil?
-
Alkaline soil (pH > 7)
- Why does the soil become alkaline?
- What plants grow in alkaline soil?
-
Slightly acidic or neutral soil (pH 5.5 - 7)
- Why is the soil slightly acidic or neutral?
- Which plants grow in slightly acidic or neutral soil?
-
Acid soil (pH < 5.5)
-
Change soil pH
- soil too acidic
- soil too alkaline
Tip: Central European soils most commonly have a slightly acidic pH of 5.5 to 6.5, and this range is also optimal for a very large proportion of our crops and ornamental plants. However, exotic or very special plants may require a more acidic or more basic soil. There are also many areas in Central Europe whose soil acidity deviates greatly from this standard. So it's worth checking the pH of your own soil - with the aim of supporting plant growth in the garden as best you can.
Determine the pH of the soil
Especially when you have just bought a garden or a piece of field, it is very interesting to find out what the pH value of the soil is. Because you can use this value to make a well-founded decision as to which plants will grow well here or whether the acidity should perhaps even be changed.
tip: For many garden owners, the lawn in particular is an important component of the garden. The appropriate pH for lawns is between 5.5 and 7.5, depending on the type of soil. There are often problems with moss, other weeds or simply poor lawn growth due to a deviating acidity. So if you check the acidity of your own soil in advance, you can save yourself a lot of frustration. The ground under existing lawns can also be improved in this way, namely by using the lime the lawn.

There are several methods of estimating soil pH. These are quite easy to apply for garden owners:
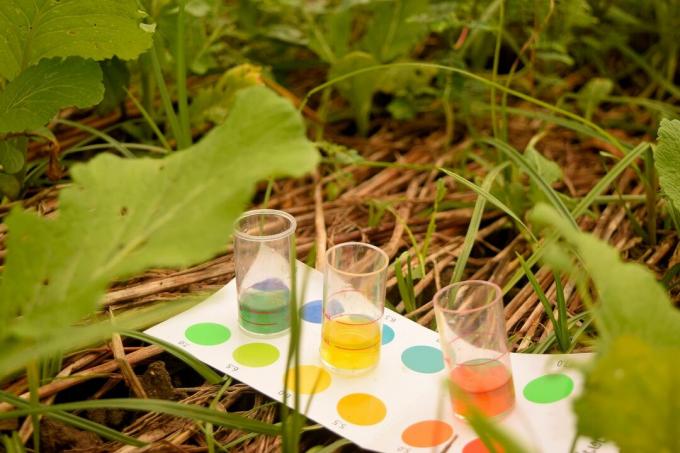
pH soil test
There is a whole range of different soil testers that you can use: For example, there are simple and rather imprecise ones pH soil tests with indicator paper or special test kits that indicate the pH value via the color change of a liquid, available. There are also digital pH value measuring devices up to highly professional laboratory tests, which, in addition to the pH value of the soil and the nutrient content, also Determine soil type.
The fact of the matter is that the particular test method affects the result you get. Simple tests use water or distilled water to measure pH, laboratories typically use calcium chloride suspensions. Digital measuring devices even measure directly in the soil by measuring the current flowing between two measuring electrodes and interpreting it as a pH value.
The measurements from specialized laboratories are the most reliable and comparable. All other methods can only be considered as an approximation, but they are usually completely sufficient in the hobby garden area.
Tip: If you do a pH test of your soil yourself using a test kit or an indicator strip make sure that you use distilled water and that the suspension is warm to 25 °C if possible is. Because the measured pH value is influenced by the temperature and substances dissolved in the water.

Indicator plants for soil pH
As mentioned above, plants always prefer a certain pH range. They die or do not germinate at all in soil that is much too acidic or alkaline, while with the right pH values they thrive or even multiply profusely.
The positive side effect is that you can use some wild plants or weeds as an indicator, i.e. "indicator", for soil properties. Good indicator plants ("bio-indicators") are of course only the genera and species that have specialized in a narrow pH range. Everyday plants such as dandelion (Taraxacum sect. ruderalia) or the Chickweed (Stellaria media), which seem to grow everywhere, are not good indicator plants because they tolerate a wide variety of conditions.
If you see any of these plants growing healthy and in large numbers in your garden, you can get a rough idea of whether your soil is acidic or alkaline:
| Biological indicators for acidic soils | Biological indicators for alkaline soils |
| yellow clover (Medicago pupulina) Hasenklee (Trifolium arvense) Little sorrel (Rumex acetosella) Small burnet (Sanguisorba minor) cornflower (Centaurea cyanus) creeping cinquefoil (Potentilla reptans) marsh valerian (Valeriana dioica) Wild Pansy (Viola tricolor) |
Charlock (Sinapsis arvensis) Field Larkspur (Consolida regalis) hyssop (Hyssopus ofcinalis) |

What does my soil pH mean?
Basically, measuring soil pH gives you a measure of how much hydrogen is in the soil and how active it is. Depending on the amount of hydrogen in relation to oxygen in the soil different compounds of these two elements in the soil solution: in particular oxonium ions (H3O+), Water (H2O) and hydroxide ions (OH–) are always present, but can be found in varying amounts depending on the degree of acidity of the soil.
| acid soil | neutral ground | basic soil | |
| PH value | 3 – 6,5 | 7 | 7,5 – 9 |
| Occurrence of hydrogen (H+) | Hydrogen is mainly as H3O+ (oxonium) found in soil. | Hydrogen is mainly as H2O (water) found in the ground. | Hydrogen is mainly available as OH- (Hydroxide) found in soil. |
| Ratio of hydrogen to oxygen | 3:1 | 2:1 | 1:1 |
An acidic soil contains a lot of oxonium, a neutral soil mainly neutral water and an alkaline soil a lot of hydroxide.
Ultimately, it is the presence of these three compounds that creates the effects on the soil. They indirectly influence, for example, the availability of nutrients, the activity of soil organisms and the extent of humus formation.

Acid soil (pH < 5.5)
On acidic soils, in which a lot of reactive oxonium is found, nutrients that are otherwise difficult to obtain become dissolved, salts and minerals decomposed and some trace nutrients such as iron, manganese and zinc are better with it accessible. However, if the acid is too strong, substances can also be released that damage most plants – such as aluminum. Fungi and fungal microorganisms thrive in rather acidic soils, while numerous soil bacteria cannot survive. This has an impact on the humus-forming processes in the soil: on acidic soil, the fungi in the soil produce a lighter, reddish-colored humus of lower quality.
Why is the soil becoming acidic?
Acidic soils form when the minerals in the soil are exposed to the constantly acidifying effects of slightly acidic rainwater, rotting organic matter, acidic fertilizers and hydrogen-secreting plant roots be able. One speaks of the so-called buffer capacity of the soil. Sandy soils, for example, are less well "buffered" than clay soils and can therefore move faster and stronger acidify - this can be observed, for example, in the moor, a purely organic soil without rock fractions. Here no rocks like limestone buffer the acidification and so the moor becomes more and more acidic. Incidentally, water saturation and waterlogging also lead to acid in the soil, because carbon dioxide from the air reacts in the absence of oxygen to carbonic acid - this is also a reason why the very wet moors are particularly acidic are.
What plants grow in acidic soil?
Only a few specialists are adapted to (very) acidic soils, such as ericaceous plants such as hydrangeas (Hydrangea), rhododendrons and azaleas (rhododendron), Blueberries (Vaccinium), lavender heathers (Pieris), pagans (Calluna, erica), many sweet grasses (Poaceae), skimmia (Skimmia) and glorious bells (Enkianthus campanulatus).

Alkaline soil (pH > 7)
Soil bacterial organisms thrive in alkaline soils, where more hydroxide is found, than in acidic soils. This in turn means that many organically stored nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphates and potassium are more readily available at high pH values because the soil organisms release them. The soil structure often improves as a result of an increasing soil pH value, the soil becomes more crumbly and loose. On extremely alkaline soils, however, important trace nutrients are hardly available, so that plant growth is hindered again and fertility decreases.
Why does the soil become alkaline?
Alkaline soils form when soil develops on very calcareous rock, classically limestone. Even soils with a high clay or silicate content can repeatedly (over)compensate for released hydrogen, so that there is only a small proportion of oxonium in the soil solution. A good example is the very fertile black soil and brown soil of the Hildesheimer Börde, whose high pH value results from the high proportion of loess in the mineral content of the soil.
What plants grow in alkaline soil?
Few plants grow particularly well in basic soil. Some cacti and succulents prefer neutral to slightly alkaline soil, as do mountain plants such as pasque flower (Pulsatilla), helichrysum (helichrysum), but also garden plants such as bulbous (Allium), salsify (Scorzonera) and lavender (Lavandula) love high pH values.

Slightly acidic or neutral soil (pH 5.5 - 7)
In the golden mean, i.e. in the weakly acidic, weakly alkaline or neutral soil, the soil structure is good and all nutrients are sufficiently available. No wonder most plants prefer such a state. If you own slightly acidic or neutral soil, you usually no longer have to work with lime or other agents, but can start fertilizing and planting directly. A large part of the soil in Germany is slightly acidic and a large part of our native plants are also adapted to it.
Why is the soil slightly acidic or neutral?
Soils with a balanced degree of acidity are able to buffer acidifying influences by using Clay minerals and metal oxides (such as iron oxide) neutralize hydrogen and thus always keep the pH between 5 and hold 8 Even small amounts of limestone are often present. In addition, humus acts as a buffer and stabilizes the pH value. Loamy, humus-rich soils on limestone, as they often occur in Germany, are therefore often slightly acidic to neutral.
Which plants grow in slightly acidic or neutral soil?
Most crops and ornamental plants prefer medium acidity. Only specialists (moorland plants, desert plants, tropical plants, ...) from distant countries or those who are adapted to very special conditions, do not do well on slightly acidic to neutral soils survive.

Tip: With the ground instead of against the ground
When the soil in your own garden is not only slightly acidic or neutral, but rather in an extreme range moved, you have two options: First, you can try to soften the soil by adding appropriate additives change. Changing the pH of large areas is often expensive, especially when the pH is extremely acidic or alkaline. In addition, the change is sometimes not permanent, but the soil returns to its individual pH value through the soil-forming materials. Secondly, if you have a highly acidic or alkaline soil, you can consider simply growing specialized plants choose those who love these conditions - and other plants, for example in tubs or raised beds with high-quality potting soil like ours Plantura organic soils to plant.

Change soil pH
Is your soil slightly too acidic or too alkaline for your purposes, or has it been out of balance due to years of poor management? If you want to permanently change the pH of your soil, you should check the pH on an annual basis and you can do the following to change the value.
soil too acidic
A soil that is slightly too acidic, for example with a pH value of 5, can easily be corrected with lime. However, the type of lime that should be used depends on the type of soil: sandy soils, for example, are easier to influence than soils rich in clay. The humus content also has an influence on the correct form and amount of lime. As a rule, the application of lime is divided into two doses, i.e. lime is applied for two years in a row. Carbonate of lime is well suited to sandy and peaty soils. Quicklime works very quickly, is even caustic and helps to increase the pH value even in heavy, clayey soils. Only a soil pH test can tell you how much lime needs to be distributed. Tests for the hobby area often contain good information on how to proceed. Another way to increase the pH value of the soil is the regular use of basic rock flour from diabase and other types of basalt.

soil too alkaline
Acidifying soil is a little more difficult than making it more alkaline. The reason for soil that is too alkaline is the rocks that form it, so lowering the pH value quickly becomes a battle against windmills that has to be carried out every year. Soils can be acidified with elemental sulphur, which is also available as so-called sulfur flower or sulfur flower, because this is converted into sulfuric acid by bacteria in the soil. Dosing requires a delicate touch: as little as 50 to 100 g of sulfur flower per square meter can lower the pH value of a medium-heavy soil by more than one unit. Light soils react more sensitively and become acidic more easily, heavy soils, especially very rich in humus and compost react much more slowly and require larger amounts of sulfur flower to become acidic will. Natural ways to acidify the soil are the use of grape pomace, acidic granite bedrock and regular mulching. If you want to save peat in the garden, but don't want to do without it entirely, you can also plant regularly Pour peat extracts: Two handfuls of peat are poured into a 10 liter watering can for a week inserted. The peat is then removed or strained and the now acidic irrigation water given to the acid-loving plants. However, the effect of this treatment is not permanent and must be repeated monthly.
Soil pH is closely related to soil type. In our special article, we explain how you can use them in your garden Determine soil type be able.

