
Power supply is also usually indispensable in gardens. A professional solution here is to lay an underground power cable, because it is invisible and not a source of accidents. But you need to know how deep a so-called underground cable has to be.
In a nutshell
- Properly laid underground cables without problems for years
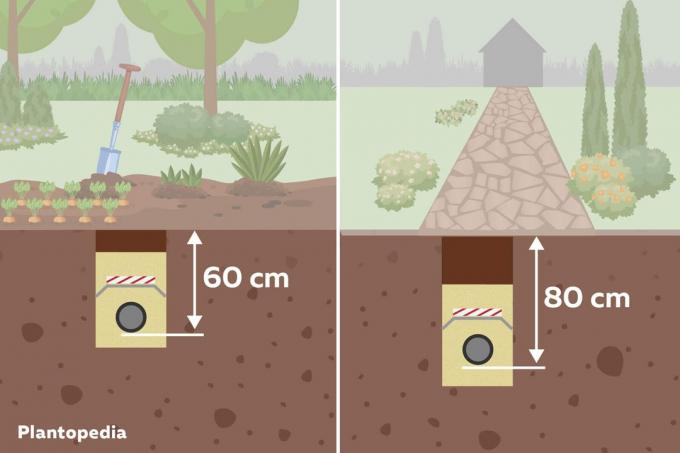
- Laying depth in the garden 60 cm
- under paths and roads 80 cm
- Laying in empty conduit recommended
- Don't forget the warning tape
Table of Contents
- Laying depth important
- Observe minimum depths
- Laying tips
- frequently asked Questions
Laying depth important
Depth is important when laying underground cables. You need to laid frost-proof so that the cables are protected against possible damage at low temperatures in winter. Frost can attack the cables in the long term and short circuits to power failures to lead. With the right installation depth, you can prevent such failures. Laid sufficiently deep, you can also continue to carry out your usual digging work in the garden.
A notice: The protection standards for wet rooms apply to underground cables. They must correspond to at least protection class IP 44. The higher the number, the better the cable is protected against moisture.
Observe minimum depths
The minimum laying depths are regulated by a VDE standard, which is defined in DIN and VDE (DKE). When laying underground cables outdoors, the DIN VDE 0100-520: 2013-06 (VDE 0100-520) for setting up low-voltage systems. Two installation depths are defined, independent of the soil conditions:
A notice: VDE is the association for electrical engineering, electronics and information technology.
| Garden and open space | paved Roads, paths, driveways, carports, etc. |
|---|---|
| – Minimum depth 60 cm – Protected from ground frost |
– there is a higher, permanent, mechanical load here – therefore faster wear and damage – Minimum depth 80 cm |
The standard mentioned contains further points for professionally laying an underground cable such as
- Laying in dug trenches
- Storage on 10 cm deep sand bed
- Cover with a layer of sand also 10 cm high
In principle, a deeper installation is also possible. However, you should consider the correspondingly higher effort in this case. Reducing the depth, in turn, can lead to higher mechanical loads on the underground cable, especially under roads, paths and driveways. The increased pressure load then causes long-term damage to the cable.
A notice: However, the specified VDE is also not legally binding. This is only the current state of the art. Basically, they only serve as a guideline for protection and safety.
Laying tips
Of course, to prevent damage and power failures, it is not enough just to know how deep an underground cable should be. How to route it correctly:
- Dig a little deeper
- Store cable on 10 cm deep bed of sand
- Lay out or roll the underground cable loosely without tensile load
- alternatively use a cable protection pipe (empty pipe).
- Pull the cable through the empty conduit
- use insulating tubes or simple spiral hoses from the hardware store for empty pipes
- above it warning tape with the inscription "Erdkabel" or similar. Ä. draw
- then cover with a 10 cm layer of sand
- now close the ditch with excavated soil

A notice: All finishing and installation work on the power cable should only be carried out by a professional.
frequently asked Questions
Three-wire underground cables and a cross-sectional area of 1.5 mm² are normally sufficient. However, if you plan to connect additional devices, then a five-core cable and a cross-sectional area of 2.5 mm² is advisable. This also prevents the need to lay an additional cable later.
On the one hand, empty conduits offer additional protection for the underground cable from the weather, rodents and great pressure from plant roots. If the soil should sink, damage to the cable can also be prevented. Furthermore, in the event of a defect in the line, the cable can be replaced easily and quickly without great effort. No new excavation work is required. When laying another empty pipe, you can also pull another cable at a later point in time without much effort.
Warning tapes are made of a durable material. They indicate where an underground cable runs and thus protect it from damage during excavation work. Alternatively, cable hoods can also be used. These fulfill the function of the warning tape and at the same time protect the underground cable from damage. They can be easily joined together using the quick lock.
