

Table of contents
- Recognize clothes moths
- eggs and larvae
- control
- Control by parasitic wasps
- prevention
- odorants for prevention
- Customized storage
- cleaning and order
Clothes moths can cause significant damage. It is therefore important to recognize and combat them as early as possible. But how does it work? Here you will find simple solutions.
Recognize clothes moths
The easiest way to recognize an infestation with clothes moths or their larvae is to regularly check clothing. Above all, natural materials of animal origin attract the pests.
These include, for example:
- down and feathers
- skins
- leather
- fur
- silk
- Wool
Clothing and shoes but also home textiles and books can be affected. Moth damage is characterized by small, round or irregular holes in the material. These arise because the larvae feed on the keratin contained therein. A visual inspection is sufficient to determine an infestation. Adult clothes moths can also attract attention, for example when they fly to a light source or are startled when a closet is opened.
eggs and larvae
Identifying the eggs and larvae is more difficult but important for long term moth control. Because it is not the adult insects that cause the damage. They just lay the nest and lay the eggs. In addition, they do not take any more food after the end of the development. Their lifespan after the larval stage is only about 18 days. A nest of 200 to 250 eggs is preferably laid in an area that meets the following criteria:
- dark
- dry
- undisturbed
- warm
These include, for example:
- spine
- cracks in upholstered furniture
- cabinets
- carpets
- chests
- folded blankets or fabrics
The real culprits are the moth larvae, which hatch from the eggs in the nest after about two weeks at room temperature. Due to their small size and inconspicuous, light yellowish-brown color, these are difficult to spot. However, white, thin threads reminiscent of cobwebs are a clear indication of an infestation. They are referred to as moth webs.

control
In order for the infestation to be recognized, a very thorough procedure is required. The following tips can help:
examine individually
It is important to check all items of clothing individually in order to find the small clutches and possibly moth webs or even larvae. Insides, folds, and folded pieces are common locations.
Search in niches
Cracks in upholstered furniture, rolled-up carpets and books that are rarely opened are popular places, as is the furthest corner of the closet.
Use pheromone traps
The adult butterflies can be caught with special pheromone traps for these moths. Egg-laying cannot be avoided in every case, but the infestation with the six to ten millimeter large insects can be determined with certainty. This variant is particularly recommended when regular checks at short intervals are not possible.
Check regularly
Due to the rapid and numerous reproduction, everything should be checked as often as possible. This is especially true if an infestation has already occurred.
Control by parasitic wasps
A particularly simple way of combating clothes moths is to use parasitic wasps or their moth larvae. They infest the harmful insects and feed on them.
The advantages of this are:
- the animals die as soon as no food source is available
- simple application
- low cost
- easily available in stores and can be ordered online
- Ichneumon wasps do not pose any danger to other creatures or textiles
- small effort
After fighting, a thorough cleaning should be carried out again. This applies to the textiles as well as to the containers in which they are stored and the environment.
Vacuum cleaners, disinfectants and hygiene detergents, for example, are well suited for this. The contents of the vacuum cleaner bag or dust container should be discarded immediately. Otherwise the moths could spread again.
prevention
As always with moths, prevention is better than cure or in this case control. On the one hand, odorants and, on the other hand, appropriate storage are decisive for this. Thorough cleaning and good order also make sense.
odorants for prevention
For both prevention and control, scents are repellent to moths.
lavender
Dried lavender in scented sachets or the essential oil of the plant dripped onto towels can be placed in the closet with the laundry.
mothballs
These balls are hung in the closet, for example, or placed between the layers of textiles and repel insects. However, the smell is often also perceived as unpleasant by people.
cedar
Coat hangers, discs, balls and shavings made of cedar wood not only spread a pleasant scent, but also efficiently repel moths.
Tip:
There are also products on the market that are odorless for humans, such as Aeroxon moth repellent. These are laid out or hung up in endangered areas and quickly become effective.
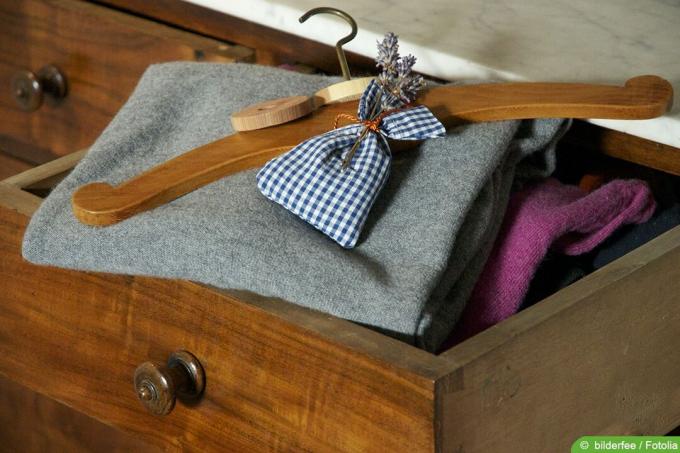

Customized storage
If clothing, shoes or other textiles are not needed for a long time, appropriate storage makes sense. Bags or bags in which a vacuum can be created are favorable, for example. This works with, among other things:
- special film and a vacuum sealer
- Plastic bags from which the air can be rolled out or squeezed out
- through special bags with a vacuum cleaner
Tip:
Alternatively, boxes and chests that are as airtight as possible can be used to protect materials of animal origin in particular.
cleaning and order
Moths, which prey on keratin and thus on shoes, clothing and other materials, prefer undisturbed areas. Regular cleaning interrupts this rest and may even remove an existing nest in the corner of the cupboard or on the carpet.
Cleaning is easier when there is order and basic cleanliness. Textiles – especially those of animal origin – should be washed or dry-cleaned before storage. This removes hair and skin cells and also changes the smell. As a result, there is less attraction for the moths.
Neat stacks also allow the closet to be checked quickly and wiped out if necessary.
 garden editorial
garden editorial I write about everything that interests me in my garden.
Learn more about crop protection
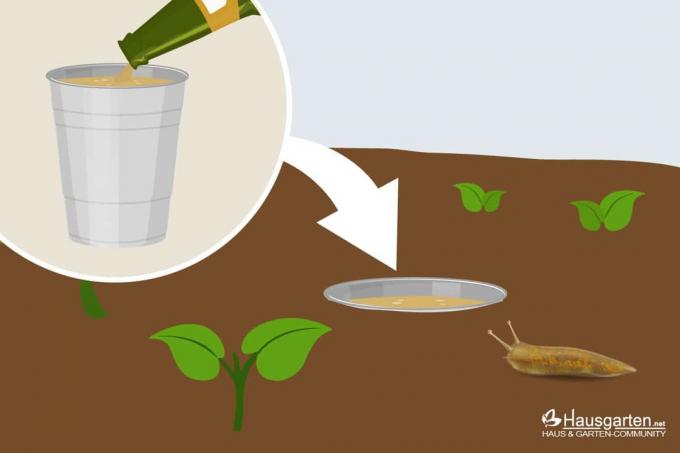
Beer trap against snails | Build it yourself or let it be?
There are several ways to banish snails from your garden beds, one of which is the beer trap. The animals smell the yeast contained in the beer and crawl into the trap and are supposed to drown in it. The alcohol in beer is also toxic.
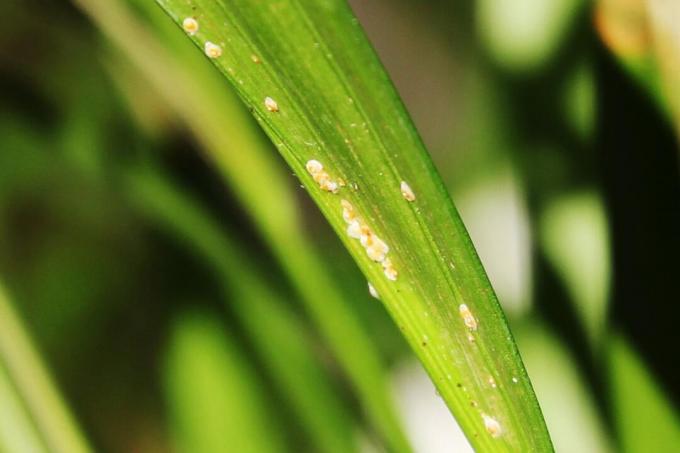

Fight scale insects: 20 home remedies
Scale insects are stubborn and feared pests because they feed on the sap of plants. In addition, they spread rapidly and do not stop at neighboring plants. However, there are various home remedies that you can use to fight the plague.

Build your own snail trap 5 tips for the garden
Snails can cause considerable damage, especially to young plants and new shoots. Building a snail trap yourself can prevent this. But what should be used as bait and how should the snail traps be constructed? We show it here.

Fighting voles in the garden: 14 tips
Controlling voles in the garden can be tedious and frustrating. With the right tools and measures, however, the effort is significantly reduced while the chances of success increase. These can also be biological and gentle so as not to pose a burden on the environment and other animals.

Cockroaches in the apartment: where do they come from and what helps?
Cockroaches in the apartment are a horror. The cockroaches are carriers of numerous pathogens and can multiply rapidly within a short period of time. To prevent an infestation, you must know the causes of the settlement or fight the insects.
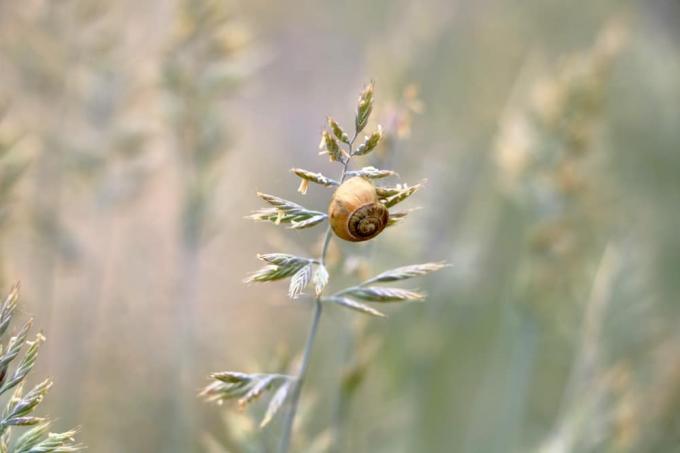

Snail fence: copper or plastic? Which effectively helps
A snail fence is a very effective means of controlling snails. You install the fence around the plants or beds you want to protect. Fences come in a variety of materials and sizes, with copper and plastic being common choices.



