

Table of contents
- shape and origin
- The static structure
- Typical roof structures for tent roofs
- The pitch of the roof
- roof coverings
- Roof structures and installations
- Distinction from other roof shapes
- Cost of a tent roof
- advantages and difficulties
Where the tent roof got its name from is unmistakable. But this roof shape has long since made it into the circle of design stylistic devices in residential building. It stands out from other roof shapes due to a number of elementary advantages. We explain these differences and also provide numerous facts worth knowing about the tent roof.
shape and origin
Of course, based on the name alone, the relationship between the tent roof and the real tent is unmistakable. But the design is also visually reminiscent of the simplest form of the tent consisting of a central pole with a tarpaulin stretched over it. The first permanent dwellings in the form of yurts, simplest huts and other forms of appearance also use this simple and effective roof form.
There is a tent roof adapted to the usually orthogonally aligned floor plans of residential buildings usually made up of four roof planes of identical pitch, centered on a central ridge point touch. This results in the almost inevitable square shape of a building covered with this roof. A surrounding lower edge of the roof reinforces the impression of a self-contained roof hood sitting on the structure. For example, a popular nickname for residential buildings with a tent roof is "mushroom house".
The static structure
From the shape with a central ridge point, it quickly becomes apparent that the tent roof, despite its visual proximity, has to follow a completely different static approach than this pitched roof:
1. Central ridge support
- Vertical derivation of the loads from the ridge point into the underlying solid components (ceiling or wall)
- From each building corner of hip rafters to the ridge point as the upper support or connection point of the rafters
- Circumferential sill as lower support point
- Rafters as supporting elements of the roof structure of the individual roof areas
2. purlin construction
- Circumferential threshold as the lower support point of the rafters
- Circumferential purlin as upper support, mostly approx. one third to quarter of the rafter length from the ridge point
- Upper rafter ends cantilever to the ridge point
- Purlins are loaded onto foundation components via supports or walls
3. Rigid frame construction
- Circumferential threshold as the lower support point of the roof construction
- Hip rafters from the corners of the building to the ridge point, supporting each other, as a rigid frame construction with no middle support
- Rafters placed on hip rafters, or connected in the same level
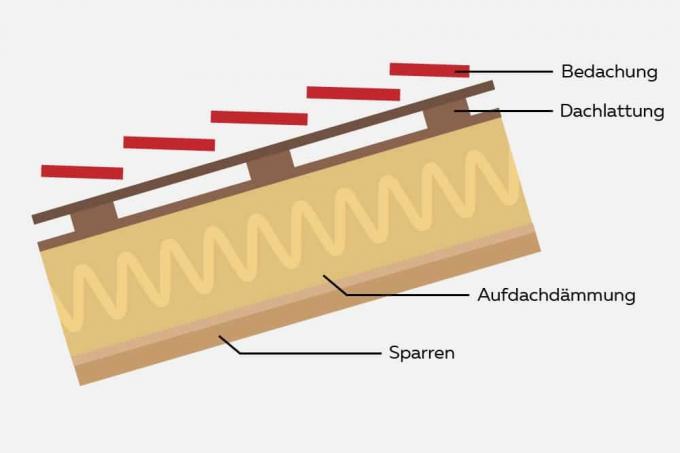
Typical roof structures for tent roofs
Constructively, possible roof systems of the tent roof are based on the proven methodology:
- Inside: Vapor diffusion-tight level against the ingress of moisture from the living space into the insulation level
- insulation layer
- Diffusion-open sub-roof to ventilate escaping moisture from the roof structure, if necessary in combination with another insulating layer
- Rear ventilation level to remove escaping water vapor
- Outside: Roof skin with substructure
Ultimately, both common options can be found in the tent roof to realize this structure in relation to the supporting structure:
1. in-roof insulation
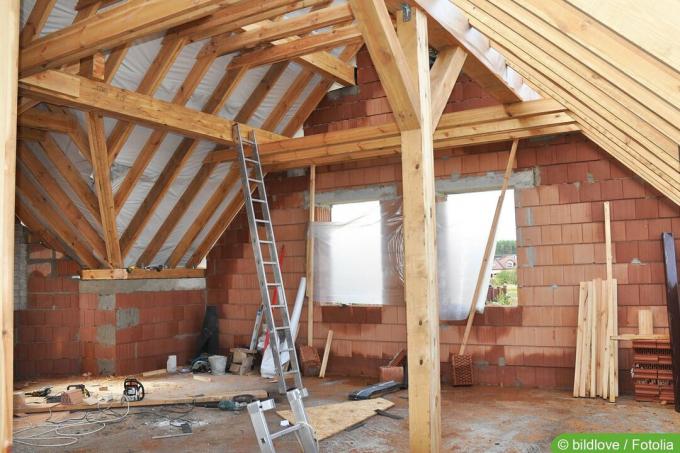
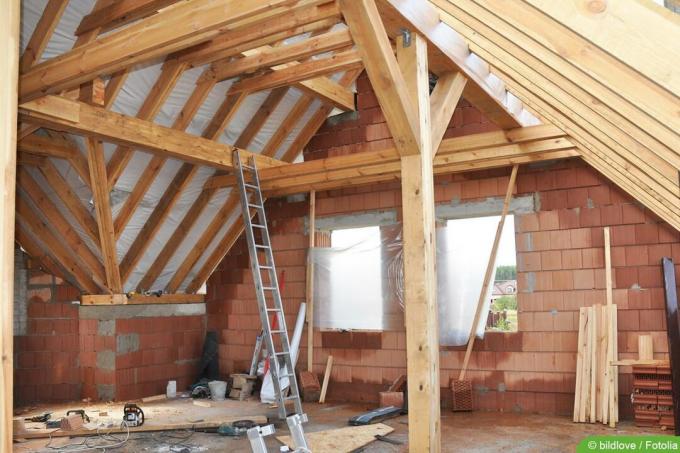
The insulation level corresponds to the rafter level. For this purpose, the insulation is inserted as a soft insulation material between the rafters. The respective limiting layers are provided below and above the rafter layer. The optically visible inner end of the roof construction is a cladding made of wood or painted, plastered or wallpapered gypsum plasterboard.
2. on-roof insulation
The insulation layer is built up on the constructive rafter layer and can be created either as soft insulation between joists or as a continuous, pressure-resistant insulation layer. As a basis for the insulation layer, a flat covering made of various wood materials must be erected on the rafters. With this variant, the supporting structure remains visible in the roof space and can be optically staged.
A NOTICE:
Contrary to numerous other roof shapes, on-roof insulation is very widespread for tent roofs. The background is the high number of constructive elements and detail points in the rafter position, which a large number of fault points in the insulation layer when installed in the construction level would.
The pitch of the roof
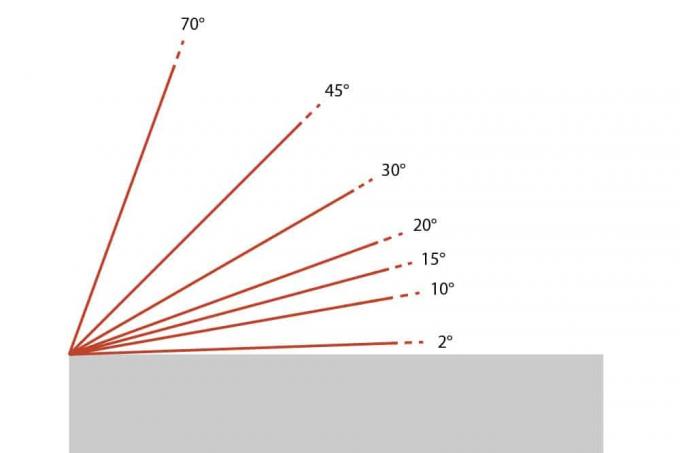
Ultimately, a tent roof can be erected in all inclination variants from 0 degrees. However, the construction only makes sense from a technical point of view from about 10 to 15 degrees, since the roof space gained is otherwise mainly taken up by structural components. Inclinations between 15 and about 30 degrees are common today. On the other hand, larger inclinations in the range of 45 degrees and more create a voluminous roof space, which, however, is very difficult to use due to the all-round inclination. In these cases, an alternative, more usable roof shape is usually chosen.
roof coverings
Depending on the pitch of the roof, a tent roof can be fitted with almost any type of roof covering. Flat coverings should be given preference to tiles or shingles, especially on small roofs otherwise countless adjustments and cuttings of individual bricks are required due to the ridge details found on all sides would be. Types of flooring that are encountered again and again are:
- Bricks and concrete roof tiles - mostly from 15 degrees, some models from 10 degrees
- Foil roofs – any roof pitch
- Gravel or green covering on foil roof - more than 10 degrees makes only limited sense
- Slate, shingles and other local roofing variants - mostly from approx. 15 to 20 degrees, depending on the substructure
A NOTICE:
Since the tent roof in residential buildings has no history worth mentioning, there are no typical, historical forms of cover, such as straw, thatch or reed.
Roof structures and installations
In principle, the individual roof surfaces of a tent roof are suitable for the construction or installation of dormer windows or roof balconies. However, the tent roof is generally used with a rather flat pitch. Supplemented by the fact that the roof areas are trimmed on all sides, there is only enough roof area left in the case of very large-format roofs to place these superstructures sensibly. In practice, even skylights are rarely found on tent roofs.
Distinction from other roof shapes
From a purely geometric point of view, the execution of a real tent roof is actually only possible on square structures. In practice, it is also generally used for floor plans that are very close to the square. However, since a real square can only very rarely be realized for a variety of reasons, numerous special forms of the tent roof cover the buildings. Most of the time they are very similar to an extremely pronounced one hip roof, in which either the ridge line was minimized to zero with different inclinations of the hip and main surfaces, or the Point ridge of the tent roof with an all-round identical slope extended to a short but linear ridge became. The exact demarcation of the tent roof from other roof shapes is ultimately difficult, but the name is secondary in terms of practical implementation anyway.
Cost of a tent roof
A reliable comparison of the costs of a tent roof against other roof shapes is hardly possible. The reason for this is the common use of this roof shape. While independent lounges are often created in gabled or hipped roofs, the tent roof often covers a fully-fledged standard floor with room-high vertical walls. However, if you take into account the other special features with regard to the floor plan requirements for buildings with a tent roof, this roof shape should at least be in relation to others roof shapes never appear more expensive on the same building.
advantages and difficulties
Of course, various aspects also have a positive impact on the tent roof, while other circumstances are rather difficult:
Advantages
- Good roofing of otherwise difficult square layouts
- Low optical weight of the roof due to all-round inclination - roof shape that appears very light
- Low roof space volume, therefore without the need for additional usable space, a good solution without an unnecessarily large amount of dead space
Disadvantages
- High constructive effort
- Numerous detail and intersection points
- Hardly any roof structures or installations possible
 Home editorial office
Home editorial office
Learn more about roof / attic

Snow blows under roof tiles: what to do?
Snow drifts often get under the roof tiles when blizzards or strong winds blow them underneath. The moisture often causes damage from meltwater. Air spaces between the roof tiles are to blame. Homeowners should now find out how to counteract this.
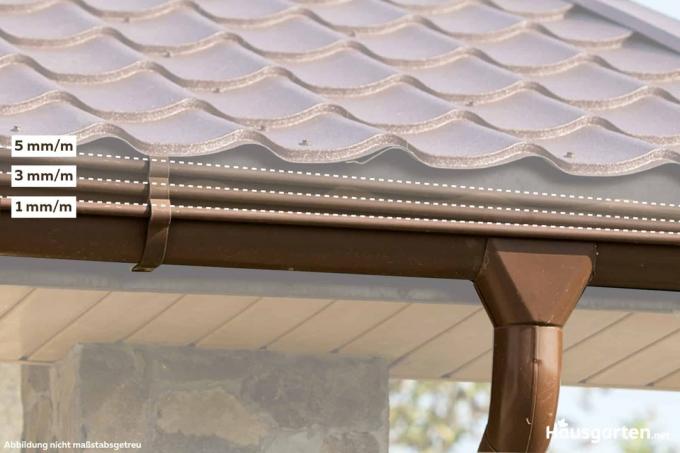

Gutter slope: the ideal gradient
For a gutter to function properly, a slope that has an ideal inclination is required. Various factors have to be taken into account. Before installation, you should find out how the gradient is to be calculated and implemented.

Which attic insulation can be walked on immediately?
Attic insulation effectively reduces heat loss from the building. If the attic is to continue to be used as storage space, the insulation should be accessible as soon as possible. A number of materials can be used for this. They each have advantages and disadvantages as well as different costs.

Bitumen stains: 6 removal tips
If you have to process bitumen, you should be careful. The black, viscous mass is sticky and adheres well to clothing, hands and all possible surfaces with which it comes into contact. With our tips you can successfully remove it.

Attic: OSB or Rauspund as roof boarding?
Both OSB and Rauspund boards are suitable as roof boarding. But what are the differences and what is better suited for the attic? Our guide answers these and other questions about the two materials.

Laying a vapor barrier: how far does the vapor barrier have to go?
Laying a vapor barrier is essential in some cases. But how far does the vapor barrier have to be installed, what is it and what are the differences? These and more questions are answered in the following guide.
