

Table of contents
- When a roof is thin
- The meaning of a diaphragm
- The pitch of the roof
- Where a diaphragm works
- Roof shapes and coverings for the diaphragm roof
- The construction
- Costs
- Advantages and disadvantages
The diaphragm can appear in many ways. It is also able to add design or functional value to the most diverse roof shapes. Here you will learn useful things about the double roof, from the structure and possible uses to additional, interesting information.
When a roof is thin
At first one might be reminded of the dwarf with the concept of the diaphragm. This assumption would also not be unreasonable, since a double roof describes the roof of a transverse building on a main building with a main roof. Ultimately, however, "Zwerch" means no more or less than "transverse", so that the diaphragm does not get its name from its dimension, but from its orientation. In architecture, the concept of the diaphragm roof is actually only found in real transverse buildings, i.e. subordinate structures that are clearly recognizable and legible at the full height of the building.
Outside of the technical language, the term is also often found in connection with dormer windows, i.e Superstructures that are surrounded on all sides by the main roof area and can only be read from the "top" on the roof are. The information given below can easily be applied to both variants, i.e. to the roofing of real transverse structures and dormer roofs. Both cases are almost exactly the same, both optically and technically.
The meaning of a diaphragm
The reasons for using a double roof may be as individual as the buildings equipped with it. However, the objective added value of this roof element can be limited to two basic areas:
1. Optical added value:
- Subdivision, zoning and outline of the main roof
- Reduction of the visual heaviness of the main roof through small, supplementary structures
2. added value in terms of use:
- straight walls instead of sloping roofs of the main roof for better furnishing
- Greater room height for lounges, access or technology (e.g. B. elevator) in the attic
The pitch of the roof
At this point, it is not about the pitch of the diaphragm itself, but about the required pitch of the roof surface from which the diaphragm should protrude. Theoretically, this is possible with any type of slope, but the flatter the slope, the larger the roof area must be. This is the only way to achieve the height difference required to accommodate the diaphragm roof due to the pitch of the roof. The difference in height not only has to be so high that the construction of the double roof disappears into it. In addition, of course, the additional gain in room height under the diaphragm roof must also be taken into account reflect again and, in addition, a certain preservation of the main roof area around the diaphragm roof is possible be. This connection can be seen quite clearly in practical examples:
1. Roof pitch 45° / house depth 8 meters (normal detached house) / central ridge:
- resulting height difference of the main roof area 5 meters
- Average roof construction height of the half roof with insulation etc. approx. 0.30 m
- Minimum height of lounge in the roof (depending on the federal state) approx. 2.20 m
- Remaining residual height of the main roof in the case of a double roof as flat roof 4.00 meters less 2.50 meters total height of the truss = 1.50 meters
2. Roof pitch 30° / house depth 8 meters (normal detached house) / central ridge:
- resulting difference in height of the main roof area 2.66 meters
- Average roof construction height of the half roof with insulation etc. approx. 0.30 m
- Minimum height of lounge in the roof (depending on the federal state) approx. 2.20 m
- Remaining residual height of the main roof with a pent roof as a flat roof 2.66 meters less 2.50 meters total height of the truss = 0.16 meters
3. Roof pitch 25° / house depth 8 meters (normal detached house) / central ridge:
- resulting height difference of the main roof area 2.22 meters
- Average roof construction height of the half roof with insulation etc. approx. 0.30 m
- Minimum height of lounge in the roof (depending on the federal state) approx. 2.20 m
- Remaining residual height of the main roof with a pent roof as a flat roof 2.22 meters less 2.50 meters total height of the truss = -0.30 meters
It quickly becomes clear that even with a minimum construction height of the diaphragm roof as a non-pitched flat roof usual living depths, an area is already reached from an inclination of 30 degrees, where a double roof is just barely functions. If the diaphragm roof is now even higher due to a different roof shape with a pitch, it can only be with a higher pitch of the main roof or a correspondingly greater depth of the roof surface up to the ridge point realize.
Where a diaphragm works

In principle, a diaphragm roof along with the associated transverse structure or roof structure can be installed anywhere realize where it emerges from a sloping roof surface with the already explained inclination can. However, its practical use shows that the usability is subject to further restrictions.
Well suited for:
- gabled roofs
- barrel roofs (with sufficient curvature)
- mansard roofs
- hipped roofs and half-hipped roofs with large remaining roof area
Moderately suitable for:
- Smaller hipped roofs and half-hipped roofs (due to insufficient remaining roof area)
Unsuitable for:
- pent roofs (since it is very difficult to reconcile the design with a clear shape and the inclination is often not sufficient)
- Flat roofs (since there is no appreciable inclination)
Roof shapes and coverings for the diaphragm roof
In fact, all common roof shapes and covering materials of modern residential buildings can be realized with the diaphragm roof. Depending on the chosen roof shape the diaphragm roof can either appear imposing or blend in unobtrusively with the main roof area. Only a few limitations to add:
- The ridge direction of saddle, hipped or barrel roofs is always orthogonal to the main roof
- Inclination on the trailing roof (inclined roof surface with the same orientation and direction of rise as the main roof) is always less than the main roof inclination
- With a hipped roof, only one-sided hipped surface is possible
For reasons of homogeneous appearance, the same covering materials are usually used for the half roof as for the main roof. Sheet metal or foil is only used if the pitch of the diaphragm roof is too flat, possibly as a contrast to the main roof.
The construction
As a rule, a diaphragm roof uses the roof structure used for the main roof for reasons of economy. Since the construction height, as already shown in the example, is often a problem, in-roof insulation with an insulating layer inserted between the rafters is often used. The interior vapor barrier and exterior underlay membrane are attached to the appropriate levels of the main roof.

From a constructive point of view, the loads of the diaphragm roof are derived directly from the solid walls below. If, on the other hand, you don't look at a real transverse building, but at a dormer, the entire dormer, including walls and roof, is usually placed as a wooden construction on the limiting rafters. The wall structure is also based on the structure of the main and intermediate roof and thus ultimately represents a kind of vertical part of the roof surface.
Costs
Of course, each diaphragm means additional costs. Compared to the main roof, these are significantly higher per cubic meter of volume created, since the proportion of the envelope area is significantly higher. Small transverse buildings to improve the usability of individual rooms can be realized for as little as 10,000 euros. If the transverse building also protrudes in front of the main building on the floors below, the costs increase accordingly.
Advantages and disadvantages
In most cases, these advantages and disadvantages have an impact on the diaphragm:
Advantages
- Higher room height for better usability
- Additional vertical walls for better furnishing in the attic
- Better exposure options through the use of normal facade windows
- Structuring and loosening up of the main roof
- Versatile in dimensions, shape and covering
Disadvantages
- High costs in relation to the space created
- In the case of small roofs, the size is severely limited
- Numerous constructive connection points on the main roof, thus complex and prone to failure
- Only with a certain roof height or inclination possible
 Home editorial office
Home editorial office
Learn more about roof / attic

Snow blows under roof tiles: what to do?
Snow drifts often get under the roof tiles when blizzards or strong winds blow them underneath. The moisture often causes damage from meltwater. Air spaces between the roof tiles are to blame. Homeowners should now find out how to counteract this.
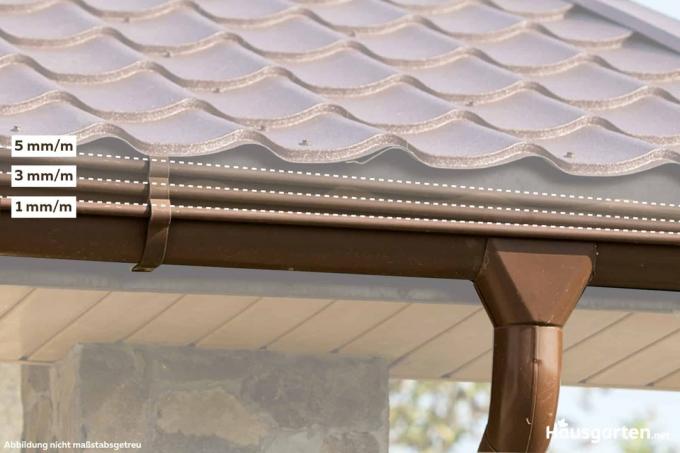

Gutter slope: the ideal gradient
For a gutter to function properly, a slope that has an ideal inclination is required. Various factors have to be taken into account. Before installation, you should find out how the gradient is to be calculated and implemented.

Which attic insulation can be walked on immediately?
Attic insulation effectively reduces heat loss from the building. If the attic is to continue to be used as storage space, the insulation should be accessible as soon as possible. A number of materials can be used for this. They each have advantages and disadvantages as well as different costs.

Bitumen stains: 6 removal tips
If you have to process bitumen, you should be careful. The black, viscous mass is sticky and adheres well to clothing, hands and all possible surfaces with which it comes into contact. With our tips you can successfully remove it.

Attic: OSB or Rauspund as roof boarding?
Both OSB and Rauspund boards are suitable as roof boarding. But what are the differences and what is better suited for the attic? Our guide answers these and other questions about the two materials.

Laying a vapor barrier: how far does the vapor barrier have to go?
Laying a vapor barrier is essential in some cases. But how far does the vapor barrier have to be installed, what is it and what are the differences? These and more questions are answered in the following guide.



