

Table of contents
- What is hidden behind the half-hipped roof?
- Classic examples of half-hipped roofs
- construction and statics
- The roof structure
- Common roof coverings
- The pitch of a half-hipped roof
- Typical superstructures and installations
- Advantages and disadvantages
Almost everyone knows the typical truncated gable view of a half-hipped roof. She usually ducks under a protruding roof overhang in search of protection. Very few people know, however, that this is a half-hipped roof. Here you will find all information about this traditional roof shape and also experience numerous advantages and disadvantages.
What is hidden behind the half-hipped roof?
The half-hipped roof is a subtype of the hipped roof. Like this one, a half-hipped roof has two large roof areas of identical inclination meeting in a ridge. The gable ends are also bounded by sloping roof surfaces that meet the centrally located ridge. In contrast to the hipped areas of the classic hipped roof, which reach up to the eaves, the hipped areas of the half-hipped roof are shortened towards the bottom. The eaves, i.e. the lower edge of the roof, jumps upwards in the gable area. As a result, the triangular saddle roof gables are not completely replaced by roof surfaces, as is the case with the hipped roof, but appear here as trapezoids cut off at the top. One could say that the half-hipped roof represents a kind of intermediate step between a gabled roof and a hipped roof.
Classic examples of half-hipped roofs
The prime example of a half-hipped roof is probably the traditional Black Forest courtyard. The cantilevered roof covers both utility and living areas and, thanks to the steep roof pitches, safely diverts the sometimes enormous masses of winter snow. The large roof overhang ensures that a working area in front of the house is protected from rain and snow. And this is exactly where the hour of the half-hipped roof comes in. While a normal hipped roof would lead to enormous shading of the entire gable wall, the Reduced half-hipped area for sufficient lighting options without overdoing the protection of the roof overhang to reduce.
construction and statics
The supporting structure of the half-hipped roof consists of the following main structural elements:
- Rafters as a supporting plane for roof covering
- First as the upper support point of the rafters
- Central purlin or central purlins as support points for the rafters in the middle of the field
- Threshold as the lower support point of the rafters
- Supports or support system (“lying chair” or “standing chair”) for load transfer from the ridge, purlins and threshold to the solid walls below
DANGER:
Contrary to the hipped roof, where all elements supporting the rafters can be designed to be continuous on all sides, at least the sill as the lower support point makes a jump in height. In most cases, the sill on the half-hipped areas is even completely omitted, so that the rafters there open only on the purlins and hip rafters between the orthogonally aligned roof surfaces lay up.
The roof structure

The structures of the historical half-hipped roofs were extremely simple. As pure weather protection over the unheated roof space, transversely arranged slats supported the roofing directly on the roof rafters. Today, however, the roof structure is much more complex (construction from the inside to the outside):
- Optical paneling, e.g. B. as wooden formwork or plasterboard planking with paint, wallpaper or plaster
- Support battens for cladding, mostly at the same time installation level for lighting etc.
- Vapor diffusion-tight layer, usually as a film material
- Construction level made of rafters and soft insulation placed between the rafters (mineral wool, cellulose, etc.)
- Rainproof sub-roof membrane, as foil or additional water-bearing insulating layer (e.g. B. wood fiber board)
- Substructure of the roof covering, in the case of bricks or roof tiles made of counter battens and battens
- roof covering
A NOTICE:
If rafters are to remain visible in the interior, there is also the option of using the insulation level either as pressure-resistant polystyrene insulation, or as soft insulation between joists at rafter level to foresee. In the case of a half-hipped roof, however, this solution is usually only used in the context of subsequent insulation, as the effort involved for the corner formations between the half-hipped area and the normal roof area, which is structurally complex and therefore also expensive to implement is.
Common roof coverings
Due to the usually quite high roof pitch on half-hipped roofs, the usual coverings are usually used for covering, which are also used on the pitched roof to be used:
- brick
- concrete roof tiles
- sheet
Regionally motivated, however, these types of coverings can also be found again and again as a historical quote and a return to the tried and tested at the same time:
- shingles
- slate
- thatch / straw
Roofing made of foil or bitumen sheets, as well as green and gravel roofs are flatter sloping roofs is technically possible, but more theoretical when you look at the examples that have been built Nature.
A NOTICE:
Depending on the selected roof covering, the required substructure can of course vary. Sheet metal coverings, in particular, usually require a flat support in the form of wooden formwork.
The pitch of a half-hipped roof
In theory, the half-hipped roof can be manufactured with almost any inclination of the main and hipped surfaces. However, the long history of this roof shape shows that common and, above all, sensible inclinations range between 35 and 50 degrees. This spectrum results in a well usable roof space and the constructive details can be created without excessive additional effort. At the same time, the roof has a healthy dimension in relation to the building below, so that design and technology go hand in hand here.
Typical superstructures and installations
Due to their mostly purely economic use in the roof space, a large number of historical half-hipped roofs do not require roof structures. Both technically and in terms of design, however, all common ones can be used due to the roof pitch Roof constructions and installations from the roof window to the dormer window to the roof balcony without any problems implement. Since the main roof surfaces compared to the ordinary hip roof are less severely trimmed due to the reduced hip areas, the half-hipped roof is even more suitable for upgrading the roof space with the elements mentioned.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of the half-hipped roof are briefly summarized as follows:
Advantages
- With common inclinations, usually generous, easily usable roof space
- Good compromise between weather protection and lighting options for the gable areas
- Visually less intense appearance than a hipped roof
- Good drainage of rain and snow at normal inclines
- Good compatibility with roof structures and roof installations
Disadvantages
- High design effort for half-hipped surfaces
- High optical weight, especially in smaller buildings with a low number of storeys
- Difficult exposure options in the roof peak due to hipped areas
 Home editorial office
Home editorial office
Learn more about roof / attic

Snow blows under roof tiles: what to do?
Snow drifts often get under the roof tiles when blizzards or strong winds blow them underneath. The moisture often causes damage from meltwater. Air spaces between the roof tiles are to blame. Homeowners should now find out how to counteract this.
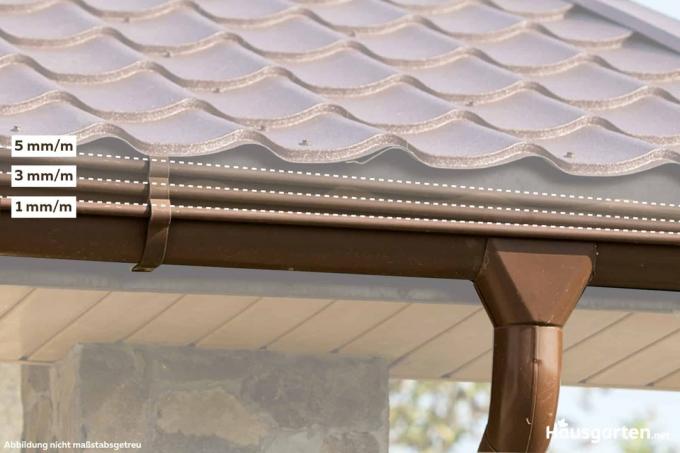

Gutter slope: the ideal gradient
For a gutter to function properly, a slope that has an ideal inclination is required. Various factors have to be taken into account. Before installation, you should find out how the gradient is to be calculated and implemented.

Which attic insulation can be walked on immediately?
Attic insulation effectively reduces heat loss from the building. If the attic is to continue to be used as storage space, the insulation should be accessible as soon as possible. A number of materials can be used for this. They each have advantages and disadvantages as well as different costs.

Bitumen stains: 6 removal tips
If you have to process bitumen, you should be careful. The black, viscous mass is sticky and adheres well to clothing, hands and all possible surfaces with which it comes into contact. With our tips you can successfully remove it.

Attic: OSB or Rauspund as roof boarding?
Both OSB and Rauspund boards are suitable as roof boarding. But what are the differences and what is better suited for the attic? Our guide answers these and other questions about the two materials.

Laying a vapor barrier: how far does the vapor barrier have to go?
Laying a vapor barrier is essential in some cases. But how far does the vapor barrier have to be installed, what is it and what are the differences? These and more questions are answered in the following guide.



