
table of contents
- Ground flea bite: Typical characteristics
- Allergic reaction
- Differentiation from grass mites
- frequently asked Questions
Every gardener knows the problem: after weeding or mowing the lawn, reddish spots appear on the skin. We show you how to recognize a flea bite and which one characteristics distinguish it from that of grass mites.
In a nutshell
- tiny leaf beetles that live near the ground
- feed on plants
- do not have bite tools
- only saliva causes redness
- recognizable by slight redness and itching
Ground flea bite: Typical characteristics
Earth fleas are not really fleas, but different types of leaf beetles. Their common characteristics are, on the one hand, their preference for everything green - and, on the other hand, their ability to jump very far compared to their tiny size. In the event of the slightest disturbance, such as typical gardening work such as weeding, raking or hoeing, the animals flee and often end up on people. Since fleas do not have biting tools, of course they cannot bite. Nevertheless, you can then discover reddish spots on the skin, which are, however, caused by an allergic reaction to the beetle's saliva. The spots may be a little itchy but not dangerous. In contrast to other gardeners such as ticks, fleas do not transmit diseases.
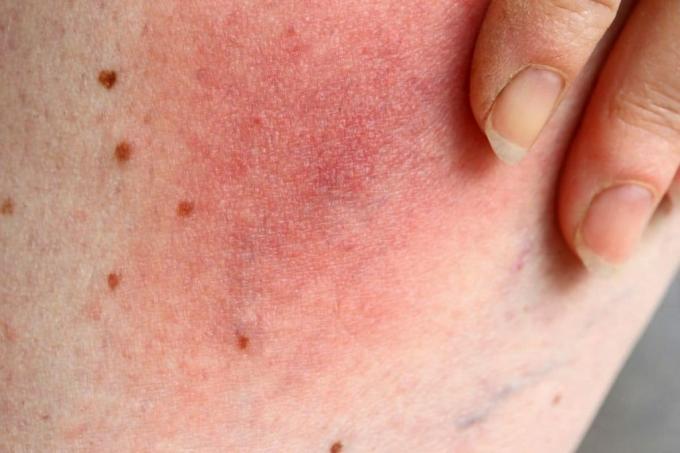
Allergic reaction
Caution is only required with these symptoms:
- severe reddening, red spots
- severe swelling
- "Bite" spot that feels hot
- Blistering
This is a strong allergic reaction that is best treated by a doctor with an antiallergic agent. You should therefore consult your family doctor, a dermatologist or an allergist.
Note: Earth fleas love hot and dry weather, which is why they are particularly active in midsummer and a "bite" when gardening is therefore very likely. You can protect yourself with long-sleeved clothing and gardening gloves.
Differentiation from grass mites
Grass mites belong to the group of arachnids and are also known as harvest mites or autumn mites. The only about three millimeters large animals live below the surface of the earth and bite the Humans do not - in contrast to their tiny, barely visible with the naked eye and very aggressive Larvae. These lurk on blades of grass and wait for human and animal hosts to pass by. You are looking for a warm, moist, well-perfused area with thin skin, which is why the characteristic wheals often in the back of the knees, the groin, the pubic area or under the Armpits occur. Once there, the mite larvae, which are only 0.2 millimeters in size, inject the skin with softening enzymes and finally suck up the cell sap and lymph. These symptoms are characteristic of a grass mite bite:
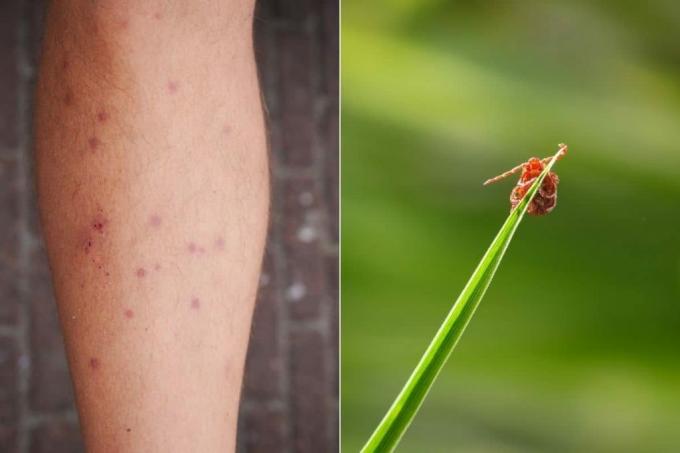

- many smaller bites next to each other
- small reddish spots with wheals
- possibly itching
- possibly mild fever
It is also typical that the symptoms mentioned only appear after about 24 hours. So should you notice such itchy wheals and the day before race mowed, grass mites are most likely the cause.
Note: Unlike many other stinging and biting insects, grass mites do not transmit disease either.
frequently asked Questions
It is best to first cool the area with a clean cloth soaked in cold water. Vinegar or a little lemon juice can also help relieve itching, but can cause a slight burning sensation. Alternatively, cut an onion open and rub the cut surface lightly back and forth on the bite site. If you do not want to use home remedies, you will find various remedies to relieve insect bites and bites in the pharmacy.
So that you don't have to be annoyed about a flea bite, prevention is the best measure. To do this, you should hoe more often, especially in useful beds, and keep the surface of the earth moist - the beetles don't like either, but many vegetables do. Mulching or foiling the beds also offers good protection. You should also put onions, garlic and spinach as companion plants in the bed to keep fleas and other pests away.
Earth fleas can be found on almost all ornamental and useful plants. However, they particularly like cruciferous plants such as cabbage, radishes, radishes, beets or Levkojen or gold lacquer. The small beetles prefer delicate, soft plant tissue, which is why they are mainly found on young leaves and shoots. They mainly stay near the ground.



