the essentials in brief
- Rapeseed oil preparations and Soft soap(€ 38.84 at Amazon *) are effective home remedies for fighting whitefly. Different plants are effective because of their essential oils or toxic ingredients.
- Often measures do not achieve the desired success because the plants are weakened by incorrect care or locations.
- Parasitic wasps(€ 69.90 at Amazon *) are parasitic beneficial insects and represent an environmentally friendly alternative to the chemical club.
- A handful of species attack certain plants, and almost any plant can be affected. They live on the underside of the leaf and are endangered by a naturally occurring fungus.
Fight whitefly with home remedies
If you have the white fly you should spray your plants with a hard jet of water. This measure works with hard-leaved or succulent plants. Soft-leaved plants should be wiped off with a damp cloth. Then it is necessary to treat the plants with home remedies.
also read
- Fight the whitefly on petunias
- That's how effective garlic is against whitefly
- Damage to the whitefly
Fighting whitefly: rapeseed oil

Rapeseed oil only harms the whitefly, it is harmless to beneficial insects, humans and pets
Rapeseed oil preparations are suitable for indoor and outdoor use, because they are beneficial and harmless to humans and pets. Mix a canola oil preparation with water and squirt the agent regularly onto the infected leaves. The pests are trapped under the film of oil and suffocate. Since the spray can clog the stomata of the leaves, you should rinse off the plants after allowing them to take effect. This is especially true for indoor plants, in which the oil film does not dissolve due to natural weather influences.
Soft soap
The product is made from rapeseed oil and potassium hydroxide solution and corrodes the skin of soft-skinned insects such as whitefly. Since it is classified as a pesticide, soft soap is not allowed to be made by yourself. You can buy soft soap in stores and prepare an aqueous solution that you use as a spray:
- Dissolve one tablespoon of soap in one liter of rainwater
- Spray directly on the pests so that leaves are dripping wet
- Insects die in their sucking posture and remain on the leaves after they die
When using it, you should take care that the fine mist does not get into your eyes. The mucous membranes become irritated and burn easily. If soft soap is dissolved in hard water, a kind of lime soap is created. It is less suitable for pest control and easily clogs the spray nozzles of spray bottles. Detergent and curd soap are not alternatives to soft soap because they are based on caustic soda. This is considered less plant-friendly.
Plants as anti-fly agents
The plant kingdom has developed natural substances that automatically keep pests away. Although planting out such plants does not completely protect against insect infestation, they still contain the populations severely. Beneficial animals and insectivorous predators can kill the remaining whiteflies.
Plants with special ingredients:
- Zinnia: Zinnias contain nicotine and attract predatory insects that eat white flies
- Nicandra: Blue Physalis contains alkaloids and withanolides that reduce pest infestation
- Monarda: Indian mint, golden balm, wild bergamot or peppermint contain disgusting essential oils
- Tanacetum: Dalmatian insect flower produces pyrethrins that paralyze the nerve center
Drive away whiteflies and keep them away
So that the annoying pests do not appear, you should make your garden as versatile as possible. There are some plants that are naturally repellent to whiteflies because of their natural ingredients. These are either suitable for planting in the greenhouse and garden, or can be used to produce pesticides.
Youtube
Essential oils
White flies can be driven away by essential oils of intensely fragrant herbs. Since the fragrances are quickly volatile, you should repeat the measures regularly and renew the herb. Fresh parts of plants are more effective than dried herbs. To extract the essential fragrances, you can brew a brew from the herb. Essential oils are the basis for sprays:
- Add mint essential oil to water
- Mix one liter of rainwater with one drop of washing-up liquid and ten drops of lavender oil
- Finely chop two cloves of garlic and pour hot water over them
- Pour 100 grams of tansy with one liter of boiling water
Mixed cultures against whitefly

If you combine cleverly, you don't need to worry about pests
Some plants have proven to be a natural defense against pests when placed in suitable mixed cultures. The vitality of the plants plays an important role. In order for such anti-pest plants to develop their full effect, they must be properly cared for. If they suffer stress from drought, waterlogging or nutrient deficiency or excess, the plants themselves develop into fly magnets. Basil makes an excellent underplant to keep the whitefly away.
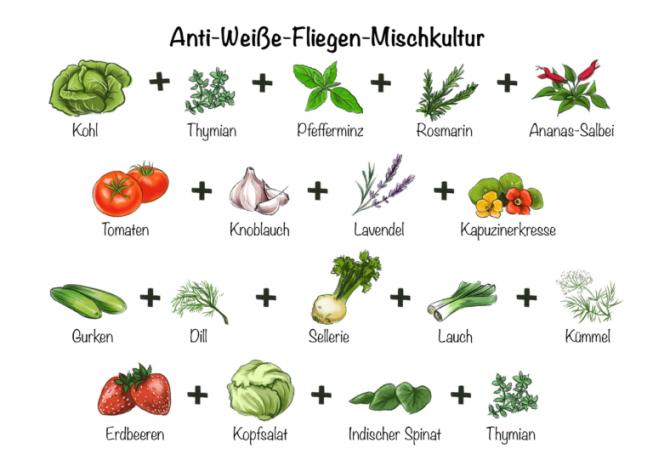
| Mixed anti-whitefly culture | Bad neighbors | |
|---|---|---|
| Cabbage | Thyme, peppermint, rosemary, pineapple sage | Strawberries, garlic, mustard, onions |
| tomatoes | Garlic, lavender, nasturtium | fennel |
| Cucumber | Dill, celery, leek, caraway seeds | Radishes, tomatoes |
| Strawberries | Lettuce, Indian spinach, thyme | Cabbage |
Parasitic wasps
With beneficial insects such as the ichneumon wasp Encarsia formosa (short: EF parasitic wasp) you can control the most common whiteflies biologically. Identify the pest beforehand to find the right parasitic wasp. The insects grow to a size of 0.5 millimeters.
Females have an ovipositor with which they stab the larvae of the whitefly and lay their eggs. The larvae that hatch from it eat the host from the inside, so that the larvae turn black. They hatch after a week Parasitic wasps. One insect can kill up to 300 whiteflies.
Use:
- Place cards with parasitic wasp larvae between the plants
- at temperatures of at least 16 degrees Celsius and a humidity of 60 percent
- not suitable for winter months due to lack of light
- after whiteflies have been fought, parasitic wasps die
When home remedies don't help

Whiteflies prefer moist, warm locations
Whiteflies prefer high humidity and temperatures above 23 degrees Celsius. They don't like drafts, but look for windless and protected areas in dense vegetation. Plants in very dry or cool locations are avoided. If, despite numerous control measures, your plants are suffering from the pests, environmental conditions could be a cause.
Increased infestation after spraying
The infestation often seems to increase after the control measure. This is because the environmental conditions change as a result of the spraying and the pests produce more eggs. You should therefore repeat spraying with rapeseed oil or soft soap solutions at intervals of ten to 14 days.
Constantly recurring infestation on indoor plants
It is not uncommon for the pests to be very persistent and no control measure brings the desired success. Often individual eggs survive in the leaf axils or in the folds of rolled leaf margins. Place the affected plants on balconies or patios during the summer months and let beneficial insects do their work. Think of sunscreen to keep the leaves from burning.
If whiteflies keep coming back, a relocation should be considered.
White flies on basil
The pests often appear on herbs in the greenhouse, although the infected plants actually have a deterrent effect. The basil is a good example of this conflict. In a healthy state and with optimal care, the herb grows vigorously and proves to be an effective deterrent. Weak and ailing plants or those specimens that are in suboptimal locations are more likely to suffer from whitefly. In the greenhouse there are two types of greenhouse whitefly and cotton or tobacco whitefly.
Getting basil pest-free:
- with at least six hours of sunshine, the disgusting aroma unfolds optimally
- a cooler location at temperatures below 18 degrees reduces the fly population
- a change of location to a well-ventilated place drives away the pests
Rapeseed oil is ineffective
Commercially available rapeseed oil does not dissolve in water without an emulsifier, so a few drops of oil in water do not result in a suitable spray. Rapeseed oil preparations contain soy lecithin, which acts as an emulsifier and dissolves the oil in water. Detergent has a similar effect, with the exact mixing ratio and the speed of mixing being decisive. An oily film does lock in the insects. However, oil droplets like to roll off, so an ecological adhesive such as Break-Thru should be mixed in.
Preparation of an oil-water solution:
- Mix ten milliliters of rapeseed oil with half a shot glass of rinsing liquid
- add a small sip of water
- slowly add a liter of water while constantly mixing
Fighting whitefly - with chemistry
There are numerous chemical remedies for whitefly. Many are based on potassium salts and have the same effect as an aqueous soft soap solution. Other products contain rapeseed oil and are expensive compared to homemade rapeseed oil sprays. So that the products work better than home remedies, various neurotoxins are added.
Common neurotoxins in pesticides:
- Acetamiprid: nicotine-like active ingredient, approved for pot, ornamental and vegetable plants
- Deltamethrin: Pyrethroid, approved for cereals, meadows, potatoes, rapeseed and beets
- Methiocarb: no longer approved as an insecticide due to its high toxicity
- Thiacloprid: nicotine-like active ingredient for combating pests and fruit pests
- Pyrethrins: natural substance with an insecticidal effect
Such neurotoxins, however, are not gentle on beneficial organisms. They not only kill pests but also wild bees, Bumblebees or important pollinators and endanger birds or aquatic life. When used in your own garden or house, they affect the health of pets and people. You should therefore refrain from using chemical agents and resort to effective home remedies or use mechanical measures.
Species of frequently infested plants

The greenhouse whitefly is only one of around 80 species of whitefly
Whiteflies are not fussy about food. They are polyphagous and come in species from more than 80 different families. The name whitefly stands for the whitefly family and includes more than 1,500 species. Many of them prefer certain plants, which can be seen in their common German name. The cabbage whitefly is a common whitefly on cabbage.
Tips
You should fight the whitefly in cool weather in the morning. At lower temperatures, the insects are less active.
background
Recognize an infestation
The first adult pests can be easily detected. When the leaves are touched, they quickly open up. Their body is covered with a floury dust made of wax particles, which makes the insects appear comparatively noticeable. It is produced by the abdominal glands and makes the body look white.
White flies belong to the group of plant lice and have four wings. They leave a sticky secretion on the leaf surfaces, which is an ideal breeding ground for sooty mildew. The sucking activities weaken the plant. If whiteflies occur en masse, yellow spots appear on the leaves. These increasingly wither and fall off if the insects are not controlled.
| scientific | colloquial | preferred plants | parasitic Encarsia species | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whitefly | Siphoninus phillyreae | Ash whitefly | Ash, apple, pear and quince trees, citrus trees | E. inaron |
| Greenhouse whitefly | Trialeurodes vaporariorum | Greenhouse Whitefly | Ornamental and useful plants, house plants | E. formosa, E. lutea |
| Silver bow tie | Bemisia tabaci | Tobacco whitefly | Vegetables and fruits of various plants, e.g. B. Tobacco, tomatoes, poinsettias | E. bimaculata, E. lutea, E. sophia, E. pergandiella, |
| Cabbage moth scale insect | Aleyrodes proletella | White fly on cabbage | Cruciferous vegetables such as alfalfa, clover or cabbage | E. tricolor |
| Citrus whitefly | Dialeurodes citri | Lemon whitefly | Citrus | E. lahorensis |
Damage to indoor plants
The plant pest Trialeurodes vaporariorum occurs preferentially in plants in rooms or greenhouses. After the females lay their eggs on the underside of the leaves, the larvae hatch and feed on the sap. They secrete honeydew so that the undersides of the leaves are covered with a sticky film. Sooty mildew can settle here when the humidity is high. A brief change of location to an airy place can help. Sensitive plants such as orchids should be treated with a jet of water.
Tips
Do not buy plants that have been treated with Confidor. The pesticide contains the active ingredient imidacloprid, which drives parasitic wasps to flight.
Plants in the garden
When fighting the sap suckers, you should not just focus on the infested crops. Broaden your view of the entire plant population. In the garden, vegetable plants are often affected by the pests when the microclimate offers favorable conditions. The insects mainly attack weakened and ailing plants. Annual herbs and balcony flowers are particularly often affected. White flies do not stop at ornamental plants and woody plants either. Occasionally weeds can be infested.
Frequently Affected Plants:
- vegetables: Kohlrabi, cucumber, broccoli
- Woods: Roses, hibiscus, boxwood
- Ornamental plants: Petunias, Rhododendron
- Fruit perennials: Strawberries
Development and threat
Whiteflies can reproduce both sexually and asexually. The females place their eggs on small stalks on the underside of the leaves, arranging them in a ring. A layer of wax protects the eggs from drying out, while the stem ensures water absorption.
Larval stages
Females hatch from the fertilized eggs, while males emerge from unfertilized eggs. The newly hatched larvae are initially free to move so that the offspring can spread. Only the following three stages are immobile. In these phases, the larvae sit tightly at one point and protect themselves with a thick layer of wax. After the fourth larval stage, the organisms pupate.
Natural enemy in the ground
A worldwide common fungus that occurs naturally in the soil poses a threat to the whitefly. The spores of the species Beauveria bassiana adhere to the outer skin of the plant pests, so that the fungal hyphae can grow into the insect after germination. They spread and deprive the harmful insect of nutrients and water. Larvae are particularly susceptible to the fungus, which also affects eggs and adult whiteflies. This makes this fungus a useful weapon against the pest.
frequently asked Questions
How do I recognize whitefly infestation
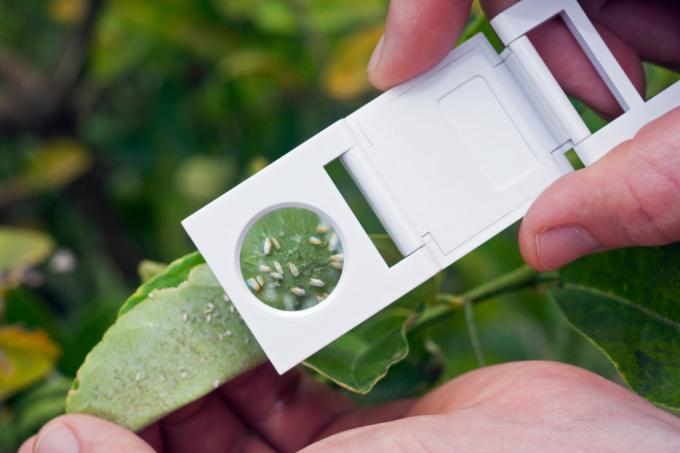

The whitefly is small, but also with the bare one eye to recognize
If you see yellow spots on the leaves, you should inspect the underside of the leaves. The adult flies quickly flee when the leaves are moved. Females lay their eggs in characteristic rings. The larvae are free to move in the initial stage and can be recognized by their whitish color with yellow, greenish or brownish nuances. In the later larval stage, they attach to the underside of the leaf and are reminiscent of smallpox. Often you will discover different stages of development on the underside of the leaves.
Typical signs of an infestation:
- Leaves turn yellow and eventually fall off
- Plant suffers from stunted growth
- Fruits are malformed
What helps against the white fly?
You can use simple methods to fight the whitefly. Home remedies should be the first choice because they often make chemical agents superfluous. An aqueous solution of soft soap has proven to be an effective agent. Essential oils have a deterrent effect and keep the insects away from your plants.
If the infestation is so strong that even home remedies no longer help, you should use beneficial insects. Ichneumon wasps are some of the most effective whitefly controls. They lay their eggs in their larvae and kill countless offspring within a short period of time. It is important that you use the correct parasitic wasp species. Each species prefers different host insects.
White flies on kale - still edible?
Basically, the cabbage is edible, as neither the pest nor its secretions are poisonous. Eggs and larvae usually cannot be washed off completely. They provide an additional source of protein, but can make sensitive people feel disgusted. The honeydew disappears when cooked. The film can be colonized by soot thaw, favored by increased air humidity. Check the kale for any rotten spots or black discoloration. Once mushrooms have settled, the vegetables should no longer be eaten.
What kind of white flies are in the potting soil?
If you have white insects in the Potting soil discover that crawl out of the substrate to the surface after casting, they are springtails. These insects are one to three millimeters in size and have no wings. They break down dead plant material and are not harmful to your indoor plants. The insects were probably brought into the planter with the compost, because they prefer to live on the compost heap. Here they turn out to be useful organisms that are involved in humus production.



