Bacillus thuringiensis as a miracle weapon against mosquitoes, boxwood moths and potato beetles - and that biologically? We'll enlighten you.

The bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis is popular both in organic farming and among hobby gardeners, because it forms the active ingredient of very environmentally friendly insecticides. Because his name is not particularly trustworthy and it is better to stay away from bacilli, we will explain you in detail in this article.
contents
-
Bacillus thuringiensis
- What exactly is Bacillus thuringiensis?
- How does Bacillus thuringiensis work?
- Bacillus thuringiensis preparations
- Advantages of Bt supplements
- Application of Bacillus thuringiensis
- Bacillus thuringiensis against the box tree moth
-
Bacillus thuringiensis: effects on other organisms
- Can Bacillus thuringiensis harm humans?
Bacillus thuringiensis
We explain what that Bacillus thuringiensis is exactly how it works and in which preparations it is contained. Then we go into the use against the box tree moth, which is important for many hobby gardeners, and clarify whether the bacterium can also damage other organisms or even humans.
What exactly is Bacillus thuringiensis?
The bacterium with the name Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is an air-breathing soil bacterium that is ubiquitous, i.e. ubiquitous around the world. When a Japanese scientist discovered a silkworm inside in 1901, he named it Bacillus sotto. In 1911, a German scientist also isolated such a bacterium from a sick caterpillar Flour moth. Because this caterpillar came from a mill in Thuringia, he named his discovery Bacillus thuringiensis - a name that has endured to this day. Since then, various subspecies and strains have been described and researched around the world. Some subspecies have a very useful property for humans: they parasitize and kill insect larvae.
How does Bacillus thuringiensis work?
- The bacterium is taken up by a feeding insect larva through the mouth opening.
- In the intestines of the larva, it forms spores in order to multiply. At the same time, crystalline toxins are formed, which in their initial form have no effect.
- If there is a suitable pH value in the intestine of the insect larva, the toxins are dissolved. They are then broken down by digestive enzymes in the larva and thus activated.
- The toxin now binds to suitable receptors on the intestinal wall of the larva. This is opened and destroyed.
- The larva dies at the same time from the destruction of its intestinal tract and from blood poisoning, which is caused by metabolic toxins from the germinating bacterial spores in the body cavity.
So you can well imagine that Bacillus thuringiensis can be used in insecticides and biocides.
Note on Bt maize and Bt soy: Behind the title as Bt maize or Bt soy lies a modification of the plant genes. A bacterial gene has been added to these maize and soy varieties, with the help of which the plant itself produces the crystalline toxin and stores it in its leaves. If a suitable harmful caterpillar eats the Bt plants, it will be killed.

Bacillus thuringiensis preparations
Four subspecies of Bacillus thuringiensis have so far been approved in plant protection products in Germany.
| Bacteria subspecies | Affected insects |
|---|---|
| B.t. kurstaki (B.t.k.) | Certain butterflies (order Lepidoptera, without Noctuidae) |
| B.t. aizawai (B.t.a.) | Certain butterflies (orders Lepidoptera, even Noctuidae) |
| B.t. israelensis (B.t.i.) | Two-winged species, including midges and mosquitoes |
| B.t. tenebionis (B.t.t.) | Leaf beetles, e.g. B. Colorado potato beetle |
Advantages of Bt supplements
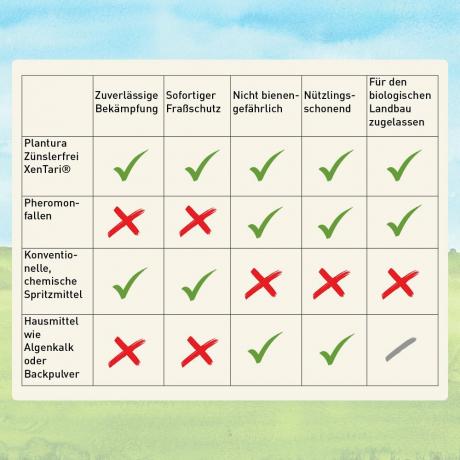
Pesticides that act as an active ingredient Bacillus thuringiensis are particularly popular in organic farming, where they can also be used many times over. Some preparations are also approved for use in the hobby garden, such as ours Plantura borer-free XenTari®. The advantages of Bt supplements are as follows:
- Unlike synthetic pesticides, they can be used frequently
- They pose hardly any danger for the user - only in individual cases do skin and / or eyes experience allergic reactions
- On the part of the target organisms, hardly any resistance is observed, even with frequent use
- Organisms that are not target organisms are not affected at all or only marginally
Note: Bt products tend to have to be applied more often, as their effect due to UV radiation and precipitation diminishes over time. Even if a new generation of pests grows up, a new application is necessary.

Application of Bacillus thuringiensis
Bacillus thuringiensis is sold as a dry powder containing inactive forms of persistence. When mixed with water, the bacteria come back to life. They can then be applied with a conventional sprayer or - in the case of B.t. israelensis against mosquitoes - to be poured into rain barrels or ponds. The effective, safe and environmentally friendly use and dosage can be found in the package insert for the product in each individual case. It is important that Bt preparations only show a good effect at temperatures above 15 ° C. Only then are beetle, butterfly and mosquito larvae sufficiently active and ingest the bacterium in sufficient quantities through feeding. When storing, it should be noted that Bt preparations can only be kept for two to three years. Opened packs can only be used for a few months, so it is worthwhile Products with sachets to buy.
Bacillus thuringiensis against the box tree moth
Bacillus thuringiensisaizawai is effective against free-eating caterpillars such as the Box tree moth (Cydalima perspectalis), Frost wrench (Operophtera brumata), Cabbage white butterfly (Pieris brassicae; P. rapae), Cabbage moth (Evergestis forficalis) and the oak processionary moth (Thaumetopoea processionea). The subspecies of the bacterium is the basis of ours Plantura borer-free XenTari®. So you can use the Fight boxwood moth biologically - completely without chemicals - and do not have to resort to agents that can unspecifically damage various insects in our environment. How the application works, when and how often ours Plantura borer-free XenTari® can and may be injected, you can find out in our associated special article. General Instructions for combating the box tree moth can also be found here.

Tip: In case you're not sure if your Boxwood (Buxus) is infested by the box tree moth, you can find out here how to remove the Recognize the moth.
Bacillus thuringiensis: effects on other organisms
The subspecies used by humans are highly specialized organisms that can therefore be used specifically to combat pests. Only when the bacterium is ingested by the appropriate insect larva will the crystalline toxins match with the host's digestive enzymes and receptors. On all other organisms which Bacillus thuringiensis its toxins have little or no effect. For this reason, there is also no endangerment for bees or other pollinating insects. In general, however, all Bt preparations must of course be handled just as carefully as any other pesticide.
Can Bacillus thuringiensis harm humans?
Even if humans and insect larvae don't have much in common, Bacillus thuringiensis occurs everywhere in our environment anyway and the subspecies used as pesticides only differ somewhat with the The effect of Bt preparations on humans was investigated in studies checked. The result was that the vast majority of test subjects showed no reaction when they Bacillus thuringiensis were massively exposed.
If you have now decided to use a preparation Bacillus thuringiensis to use against pests such as the boxwood moth, you will find all information about our here Plantura borer-free XenTari®.



