
table of contents
- Vertical gardens
- The construction
- The layers
- frequently asked Questions
A raised bed is the ingenious solution to ensure a great harvest success with little space. Which soil is used for the individual layers in the raised bed? We have the most important tips for you!
In a nutshell
- Raised beds save space and are easy on the back
- Mixed cultures of herbs, vegetables and ornamental plants are possible
- optimal nutrient supply through layer system
- perfect for gardens with nutrient-poor soil
- less pest infestation
Vertical gardens
The advantages of raised beds are obvious. A raised bed saves space, is easy on the back and uses the advantages of a mixed culture. The soil quality can be perfectly adapted to the needs of the plants. If you have a garden with poor soil quality, a raised bed gives you the chance to create the conditions for demanding plants.
Raised beds protect against the penetration of pests. Snails, for example, have a hard time getting to the plants at high altitude. A pad made of rabbit wire protects against voles and other rodents. Then you can start layering your raised bed with the right soil.

The construction
Raised beds are already offered in prefabricated form in specialist garden shops. With a little manual skill, you can also build your raised bed yourself or use simple kits.
Raised bed constructions from:
- wood
- stone
- metal
- Textile bags
- plastic
Raised beds are ideal for upcycling. Old, no longer usable wooden pallets, potato boxes, defective rain barrels, jute or plastic sacks and much more can be converted into raised beds. The internet is full of ideas!
Tip: Raised beds equipped with rollers are a good idea. They make it possible to move the bed to another location if necessary.
The layers
Below is the Layer structure and the soil you need for your raised bed. To protect against voles, a close-meshed wire mesh is suitable as the start of the raised bed layers.
- Pruning - 30 centimeters
- Branches and rough pruning should be piled up 25 to 30 centimeters high. This composition prevents waterlogging and ensures good ventilation. The ventilation accelerates the rotting and humus formation.
- Branches and rough pruning should be piled up 25 to 30 centimeters high. This composition prevents waterlogging and ensures good ventilation. The ventilation accelerates the rotting and humus formation.
- Chopped wood - 25 centimeters
- Now layer wood chips and fine shrub cuttings over the coarse pruning. Even small branches can be included. This layer prevents the finer substrate of the overlying layers from slipping through.
- Now layer wood chips and fine shrub cuttings over the coarse pruning. Even small branches can be included. This layer prevents the finer substrate of the overlying layers from slipping through.
- Coarse compost - 20 centimeters
- A layer of coarse compost provides the bed with heat. You can also use manure.
- A layer of coarse compost provides the bed with heat. You can also use manure.
- Compost soil - 15 centimeters
- This is followed by a layer of fresh, sieved compost soil. This soil contains many nutrients and forms a good basis for the development of plants.
- This is followed by a layer of fresh, sieved compost soil. This soil contains many nutrients and forms a good basis for the development of plants.
- High-quality flower or vegetable soil - 10 to 15 centimeters
- Use a layer of high-quality soil to plant the raised bed.
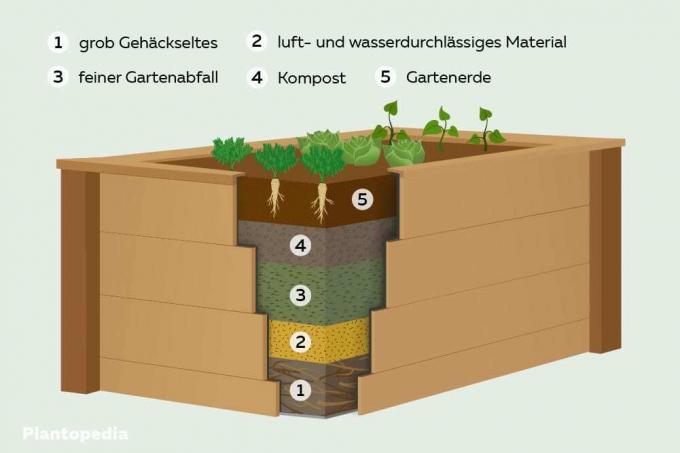
Note: You can think of raised beds as a kind of composter. The composition of the individual layers becomes finer and finer from bottom to top. The lower, coarse layers gradually rot and form valuable humus. The upper layers slide behind.
frequently asked Questions
The back-friendly, simple processing is one of the most decisive advantages of a raised bed. In order to take advantage of this, the bed should be about waist-high. One assumes an optimal height of about one meter.
In principle, you can cultivate almost all plants in a vertical bed. Mostly it is used to grow vegetables. Smaller tomato varieties, but also radishes, kohlrabi, beans or even plants that take up a lot of space such as pumpkin or zucchini thrive perfectly on raised beds. Be careful not to grow varieties that are too tall, so as not to complicate the harvest.
Raised beds are ideal for mixed cultivation. Combine plants that need similar nutrients. Be sure to place the smaller plants around the edges.
Raised beds cannot only be made from wood and natural materials. Durable constructions made of stone are possible. These can be used as an alternative to walls. Metal baskets, so-called gabions, are ideal for raised beds.
