By refining an apple, you can bring a new variety into the garden. We explain what grafting apple trees and grafting apple trees mean.

Have you discovered a new favorite apple and want to harvest it from the apple tree in your own garden in the future? What could be more obvious than storing a few seeds and skilfully sowing them? Actually nothing - if that would be Apple (Malus domestica) not a cross-fertilizer. In order for the blossoms of an apple tree to develop into fruit, the pollen of another variety has to hit the stigma of the blossom. As a result, the genetic material is essentially a mixture of mother and father trees. As a result, there will be a colorful mix of different properties in the next generation that develops from the seeds sown. However, in order to reproduce the desired variety quickly and correctly, the method of grafting is used.
contents
- Refining: why refining and what is it?
- Refining apple trees: the right time
- Refining the apple tree: the base
- Refining the apple tree: noble rice and noble eye
- How do you refine an apple tree?
-
Refining the apple tree: the procedure
- Winter finishing
- Summer finishing
- Maintain apple tree after grafting
Refining: why refining and what is it?
Grafting is about propagating a certain variety. The main interest is the true-to-variety propagation. Genuine variety means that the propagated offspring corresponds exactly to the same variety as the mother variety to be propagated. Unfortunately, since the apple is a cross-pollinator, this cannot be achieved through seed reproduction. In the end, a clone of the mother plant is created when grafting - just like when propagating with cuttings or cuttings. The variety with the desired fruit characteristics - the so-called noble variety - is combined with another plant with specific growth characteristics - the rootstock. To put it simply, the noble variety grows together with the base in order to combine the properties of these two varieties. There are different techniques for doing this, and things can go wrong and it is not uncommon for the base and the noble variety not to grow together. This can either be due to the fact that the rootstock and noble variety do not go well together genetically or simply because there is a lack of practice in refining.

So why all the trouble and risk so that in the end everything is for the cat? Unfortunately, other propagation methods are not suitable for propagating true to the variety (sowing) or lead to inferior results (cuttings, offshoots). In addition, by refining the noble variety, you can help achieve certain growth characteristics: Trees are short for plantations, stability in trees for orchards - these properties are determined by the substrate. In addition, apple trees propagated through grafting bloom and fruit much earlier than through seeds increased plants - with the latter you can get 12 years on the first high-yielding one Wait for the harvest period.
The advantages of grafting apple trees at a glance:
- Varietal propagation
- Good growth properties of the rootstock can be combined with good fruit properties of the noble variety
- Reduced time from propagation to the first blossom and harvest of apples

Tip: Of course, it's not just the rootstock that influences how healthy and productive an apple tree is. The location, and especially the soil, also has a major influence. In order to revive a less fertile soil and to give the apple tree the best conditions for growing on or on after grafting, you can use a soil fertilizer like the Plantura organic soil activator use.
Refining apple trees: the right time
There are two different times of the year for grafting apple trees. A distinction is made between winter processing (December to March / April) and summer processing (July / August). In summer, grafting techniques can be used that require loosening the bark, which is not possible in winter. The physiological principle, however, is the same: the cambium - that is the divisible tissue from which the Forming the main vessels of the tree - the two types are connected with the respective technology in such a way that they are connected to one another grown together.

Refining the apple tree: the base
In order to refine, you need a pad - or even better, a few more if you need several attempts due to lack of practice. The rootstock is an apple variety that is only relevant in terms of its growth form, its roots and their resilience or even resistance to diseases and pathogens is cultivated became. It is not relevant which fruits, flowers or leaves the rootstock would bear. After all, the rootstock will never bear fruit itself - only the noble variety that has grown together with it. However, the document has at least two important tasks:
- The vigor of the rootstock also influences the growth of the noble variety: Slowly growing rootstocks lead to overall smaller fruit trees that are easier to care for and harvest. In return, these fruit trees are less stable, so they may need a tree connection. Rapidly growing rootstocks lead to large fruit trees, which, for example, have many advantages in extensive orchards and orchards and are both stable and robust.
- The underlay determines how well the fruit tree can cope with the existing soil conditions. Some bases are predestined for wet, heavy or light, sandy soils. Other bases are particularly good at warding off soil-borne diseases or pests.
In summary, the following properties of a grafted apple tree can be influenced by the underlay:
- Growth habit and vigor (weak / strong vigorous)
- Stability of the tree
- Location requirements
- Trunk shape: Depending on the height at which the base is cut off for finishing
- Resistance especially to soil borne diseases
- Fruit quality
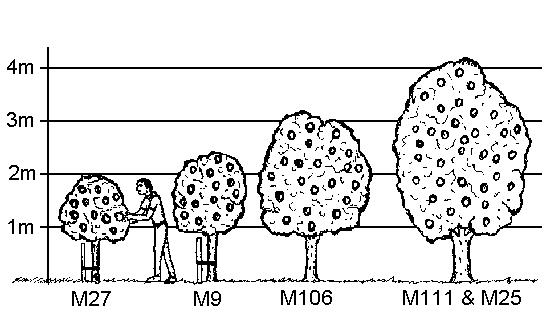
Since the documents are of particular interest for commercial horticulture, they often have more technical names. You will look in vain for descriptive terms such as 'Golden Delicious' or 'Goldparmäne'. Here is a small selection of recommended documents:
- ′ M 9 ‘: weak to medium strong growing; medium-sized trees for the home garden
- ′ M 25 ‘: strong growing; Half trunks / high trunks for the meadow
- ′ M7 ′: medium-strong growth; medium-sized trees for the home garden
- ′ M 27 ‘: slow growing; small trees / tub trees for small gardens or intensive plantation cultivation
Refining the apple tree: noble rice and noble eye
The parts of the plant that come from the apple variety whose excellent fruits you want to propagate are called "noble rice" or "noble eye". A noble rice is an approximately 10 cm long section of a shoot of the noble variety. A noble eye, on the other hand, is a single vegetative bud, which, however, can be taken from a noble rice. Depending on the refining method used, you have to choose noble rice or noble eye. Since noble vines usually comprise several noble eyes, more refinements can be carried out by propagation via noble eyes than with noble veins.

Only well-matured annual shoots with short bud spacings are considered as noble spikes. These shoots can be found in the outer, well-sunlit area of the crown. With winter processing, the vines are already collected in December or January and initially stored in a cool and dark place. If a greenhouse with heating is available, it can also be refined directly. In the case of summer grafting between July and August, the vines are harvested as soon as possible before grafting. Well-ripened annual shoots are also harvested here. Logically these are just leafy. Except for a small piece of the petiole, the leaves are removed with rose scissors and the small stipules are also plucked off by hand. The vines are now ready for summer processing and can even be stored in a cool, dark place for a short time - but if possible, but no longer than three days.
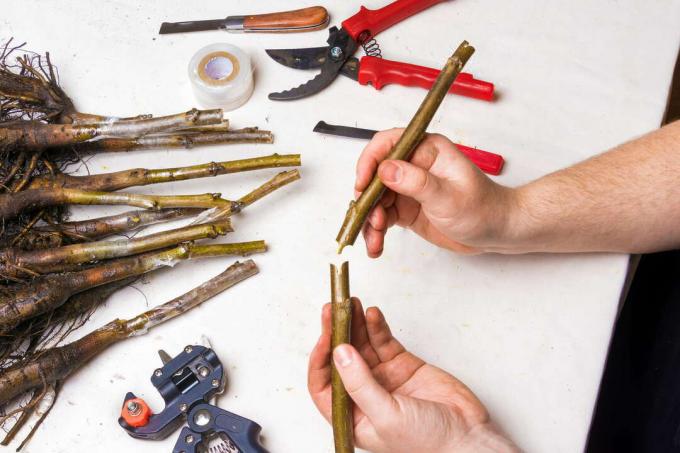
How do you refine an apple tree?
How to graft an apple tree depends on several conditions:
- At what time of the year should it be refined?
- What is the diameter of the rootstock and the noble rice?
- How much plant material of the noble variety is available for grafting?
Of course, for a special job like finishing you also need a lot of special tools:
- Very sharp knife, preferably a special finishing knife
- Rose shears
- Finishing rubbers to connect the finishing point
- If necessary, wax to smooth the finishing point

Refining the apple tree: the procedure
When refining apple trees - regardless of the method - make sure that the two refining partners are perfectly on top of each other and that there are no gaps. This increases the likelihood that the guide vessels and the divisible cambium of both refining partners will grow together quickly and well. In addition, the risk of infestation with diseases or pests via the grafting point can be minimized. To avoid unnecessary contamination of the interfaces, do not touch the areas with your fingers if possible. The exact procedure when grafting apple trees depends of course on which grafting method you choose. We take a closer look at the various methods.
Tip: Both noble rice and the base are damaged during processing and form wound tissue at this point, so-called callus. It arises exactly where the plants will later grow together: on the cambium. The production of callus creates a high pressure between the assembled elements. It is therefore very important that the finishing point is always squeezed very strongly by finishing rubbers or wound closures!
Winter finishing
Winter refinements are only carried out on bases that grow in pots. In this way, the assembled plant can calmly establish the bond after the procedure - for example in a bright hallway or a cool winter garden.
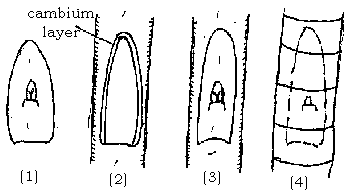
copulation
During copulation, the base and rice are cut diagonally with the same diameter so that the cut surfaces fit together perfectly. The cut should be about two inches long. The oblique cut increases the contact area so that the base and the noble variety can grow together over a larger area and thus more stably. The method can be carried out very well in winter, as no leaves have to be removed from the noble rice at this time.
- Select the base and rice with the same diameter.
- Provide the base and the noble rice with an oblique, approx. 5 cm long cut.
- Join the base and rice at the cut surfaces and connect very firmly with raffia or a finishing rubber.
- Spread the finishing point with a finishing wax.

Goat's foot method
The goat's foot method is very suitable if you only have a base with a significantly larger diameter than the noble rice. A wedge-shaped piece like a cake is cut out of the decapitated base. Make sure that the cut is pointed from top to bottom. The noble rice is sharpened on one side according to the wedge shape of the base.
- Base about twice the diameter of the noble rice.
- Cut on the base:
Two oblique cuts from top to bottom so that a 3 - 4 cm long wedge (goat's foot) is cut out. - Cut on noble rice:
Shape the noble rice with two diagonal cuts into a counter wedge of the goat's foot so that the wedge of the noble rice fits exactly into the wedge of the base. - Make sure that the cambium (green layer of the bark) of the noble rice lies on the cambium of the base and that there is no gap.
- Fix the connection point between the base and the rice with raffia and coat with finishing wax.



Plug (gap plug)
With split grafting, a significantly thinner noble rice is grafted into a thick base. For this purpose, a vertical, approximately five centimeter long cut is made in the edge area over the entire surface of the graft head in the just cut graft head. This creates a tongue on the surface that can be carefully loosened so that a gap is created. The thin noble rice is cut to a point on both sides to a length that corresponds to the gap in the base. The wedge-shaped noble rice can simply be inserted into the gap in the base, with the one on the outside Edge has to happen so that the cambia and vessels of the base and noble rice grow together at all can.
- Base cut: vertical cut about 5 cm long over the entire surface of the graft head; It is an advantage if you do not cut in the middle but rather in the edge area.
- Cut noble rice: Point the length of the base cut into an even wedge on both sides.
- Bring the base and rice together, connect with raffia and spread with finishing wax.
Tip: A noble rice can also be grafted onto the graft head of the base on both marginal sides of the split cut. Then one speaks of "double gap plug". On the one hand, you can directly create a kind of branching, on the other hand, it is theoretically also possible to combine two different types of noble on one base.
Summer finishing
The special thing about summer refinements is that at this time the bark is soft and flexible, so that some refinement methods are only possible at this time.
Okulation: noble eye instead of noble rice
During the inoculation, all that is needed is a precious eye to be placed on the surface. The name - derived from the Latin "oculus" for "eye" - says it all. Since the thinly cut noble eyes are pushed under the bark of the base, the bark of the apple tree has to "loosen". This is the case from around the end of July to the end of August.

- Prepare precious trip as described above: Approx. 1 cm thick, annual and well developed; Cut the leaves off and use them immediately.
- Cut the noble eyes flat under the vegetative bud out of the rice to a length of about 3 cm; light greenish cambium must be included and exposed (remove wooden parts if necessary).
- Make a 1 - 2 cm long, horizontal cut in the ground; make a cut in the middle vertically downwards in the length of the noble eye; this T-cut is to be made relatively superficially only in the bark, so that the light-green cambium of the base is not damaged.
- Insertion of the eye: It is better not to touch the inner side of the precious eye so as not to contaminate it. Carefully lift the bark under the T-cut with a knife and push your eye in as deeply as possible. The noble eye should be in the middle. Fix the spot at the top and bottom with finishing rubber, but the eye must remain free. You can also use a special rubber ooculation fastener (Fleischhauer fast oculation fastener).
Chip refinement
Chip refinement or “chip budding” is, in principle, a modification of the oculation. A noble eye is also used instead of a noble rice. However, with the chip refinement, the bark is not loosened, but rather a piece corresponding to the noble eye is cut out of the base relatively flat. The method is therefore independent of the loosening of the bark and could also be used in the winter months.
- Cut a uniform piece of wood from the rice and the base. In the case of noble rice, the chip consists of the bud and the surrounding bark; in contrast to the ooculation, the part of the underlying wood is not detached here.
- Inserting the chip: The chip is inserted into the appropriately cut notch on the base. Fix the spot with finishing rubber and then spread it with melted finishing wax. Caution: Here too, the bud must be exposed.
Plug behind the bark
We have already got to know the grafting in the gap as winter finishing. Alternatively, you can graft a noble rice behind the bark. Since the bark has to loosen for this, this grafting method is carried out in summer. The method is suitable for rootstocks and veins with significantly different diameters.
- Cutting noble rice: The noble rice is prepared as usual for summer refinements. In order to graft it onto the base, an approximately 5 cm long, inclined copulation cut is made.
- Cutting the underlay: The underlay tree is decapitated and a straight plug head is created. With a downward vertical cut starting from the plug head - in the corresponding one The length of the area of the copulation cut of the noble rice - carefully becomes the bark of the base solved.
- The rice is carefully pushed under the bark of the base so that the cut surface is flush with the cambium of the base.
- Connect the finishing point with the finishing rubber and spread it with melted finishing wax.
tip: As with fissure grafting, several edible vines can be grafted onto a base at the same time by loosening the bark of the base in several places. However, you should not make more than two to three cuts in order not to strain the surface too much.
Maintain apple tree after grafting
Even if it appears to have been grafted well, that is no guarantee that the two plants will grow together. Even after grafting, an apple tree still needs care and attention. Overwinter the refinements carried out in winter in a bright, frost-free room. Refinements carried out in summer should be protected from excessive exposure to the sun and should definitely be adequately watered. Not infrequently does not only sprout the noble variety, but also the rootstock. However, this is wasted energy and also promotes that the substrate repels the noble variety: therefore always cut off all shoots that sprout below the refinement point.

If the noble variety sprouts, the intergrowth has come about for the time being, but is not yet stable. If, even after a whole year, the special finishing rubber does not come off by itself due to the sun's rays, you have to cut it open to avoid constricting the tree.
tip: If you have refined your noble variety in the winter refinement on a potted base, the planting is due next May after the winter frosts have definitely come to an end. When planting apple trees, it is beneficial to give the young tree fertile soil like ours Plantura organic universal soil to promote healthy growth in the early years - after all, the small tree cannot yet take root as deeply and take care of itself worse.
In general, it is important to prune the apple tree regularly and skillfully in order to give it a stately crown. Like you one Cut the apple tree correctly, you can find out in our suitable special article.
