
table of contents
- Pruning
- Cut maple
- preparation
- cut
- Regular pruning
- Thin out
The maple, scientifically also known as acer, is considered a decorative and at the same time easy-care tree. It is not for nothing that it can be found in countless public and private green spaces. The well-known trees with their distinctive, five-pointed leaves are also very popular in front gardens and gardens. However, even insensitive trees require care and have to be pruned regularly. We'll tell you in simple, easy-to-follow steps what you need to consider when cutting maple.
Pruning
Before you can actually jump on your maple with the following instructions, you should know a few things that are generally to be considered when pruning a tree. For example, if you are aware of the influence of cutting time and shape on future growth, you can By properly cutting the maple not only trim it in shape, but also significantly reduce the future effort to decrease.
- Pruning in autumn: promotes growth and stimulates strong shoot formation
- Pruning in summer: inhibits growth and can curb excessive growth
- Temperature: do not cut in frost, otherwise frostbite at interfaces can damage twigs or entire branches
- Sun: cut when the weather is overcast, excessive drying out and damage to the interfaces due to intensive sun exposure
- Precipitation: wait for dry weather, since cutting back when it rains leads to the entry of pathogens and at the same time to bleeding of the interface
- Sealing: with "normal" branch thicknesses, no wound sealing is necessary, as this naturally dries out the interface prevents and numerous fungi and diseases good development opportunities offers
- Cuttings: If the wood is undamaged, it can be chopped well and used as a ground cover, but in the case of disease or fungal attack, it must be disposed of or burned

Attention: Since the maple is one of the trees with a strong sap, intensive pruning should always take place between autumn and January at the latest. Inhibiting spring prunings, on the other hand, should be kept to a minimum in order to avoid excessive bleeding and the resulting damage! Exceptions are the field maple and the Asian maple. These two special forms of the Acer family can be easily cut into shape in spring, or even well after they have sprouted in early summer.
Cut maple
In general, the representatives of the Acer family are considered to be slow-growing trees. A maple generally rarely needs a cut and in many cases even gets by without cutting at all. Only then, if the tree is too big or leads to undesirable shading due to its expansive shape, a shape and boundary cut should be made. The following guide explains how to do this.
preparation
Before you even get down to business on the maple, you should make all the necessary preparations in order to proceed later with the actual cut efficiently and without unnecessary surprises can.
- Clean and disinfect tools in order to remove any pathogens that may be present in other cut woods
- Sharpen the cutting edge if necessary, as smooth cuts offer fewer attack surfaces for diseases and fungi
- Clear the area under the tree to avoid possible tripping hazards, etc. to eliminate
- Check the ladder and, if necessary, use material for a safe stand (e. B. Provide wood for underlay on soft ground)
tip: Large and bulky ladders in particular can often be moved alone, but for the first erection you should definitely seek the help of a second person. If the stability is not given, all subsequent work steps will otherwise suffer.
cut
The actual cutting can be broken down into two different topics. Although it is ultimately always a question of removing wood from the maple, the work can be done by dividing it up different foci are systematized and therefore well structured and clear for beginners as well as professionals be designed.
Regular pruning
If the crown of the maple is to be kept in check, this regular, but usually not annual cut is based on the annual wood. This means that the wood that has grown in the past year is removed. On the one hand, the tree is not weakened by interfering with older and more pronounced structures, on the other hand, it is precisely this wood that makes the crown more and more lush and expansive on the outside makes appear.

- Define goals: Curb growth when space is limited
- Recognize annual wood: mostly lighter, thinner and smoother bark
- Define interfaces: Always place branches that are too long a few millimeters above leaf knots or sleeping eyes
- Cut: Always make cuts at a slight angle so that rainwater and escaping juice can flow off and drip off the cut surface
- Wound sealing: not mandatory
Thin out
The goal when thinning out the tree, however, is not to delimit the crown, but to create free spaces in the Inside the crown to ensure the exposure and ventilation of the foliage there, or to close it again to enhance. Contrary to the pruning, the focus here is not on the annual, but specifically on the perennial wood. Because even if the maple tree is regularly kept in check, individual older branches can increase in volume to such an extent that the maple ultimately hinders itself. Thus, he severely limits his ability to generate energy by means of photosynthesis by competing with himself for sunlight.

- Define goals: Distance to narrow branches in the interior of the crown
- Identify the waste wood to be removed: no clear identification of the "unfavorable" branches possible, remove several branches in the middle when standing close together in order to benefit all surrounding branches
- Define interfaces: Remove branches directly from the trunk, as new shoots from old wood rarely occur
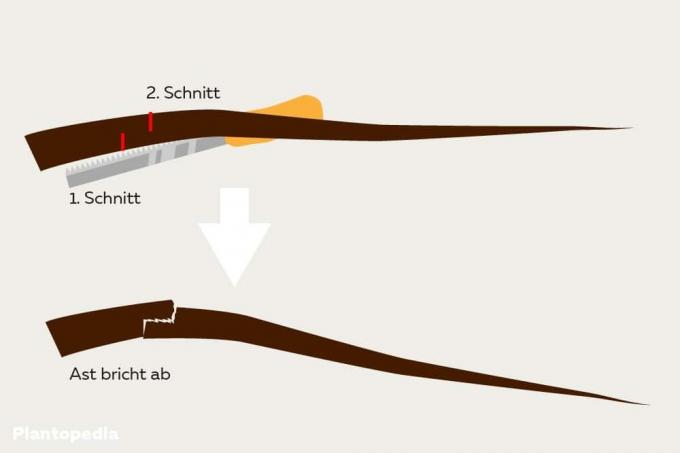
- Cut: Cut about 30 to 50 centimeters from the trunk of the branch from the bottom to the middle of the branch, then about 10 centimeters Cut further away from the trunk from above until the branch breaks off, then cut off the relieved branch roots on the trunk
-
Wound sealing: only necessary for very large cuts, e.g. B. when removing central leading branches or removing single trunks from Zwieseln
Special forms of the maple cut - then a cut is absolutely necessary
There are a few exceptions in which a pruning of the maple tree is absolutely necessary:
- After replanting bare-root young trees - then shorten all shoots by a quarter to a third
- After transplanting - compensate for the root mass lost by transplanting also in the case of the crown by pruning proportionally
- In the event of illness - remove affected branches to prevent the pathogen from spreading


